Acaricide
FRAC X
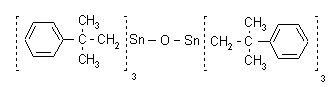
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenbutatin oxide (BSI, E-ISO, JMAF); fenbutatin-oxyde ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name bis[tris(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin] oxide
Chemical Abstracts name hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannoxane
Other names hexakis CAS RN [13356-08-6] EEC no. 236-407-7 Development codes SD 14 114 (Shell) Official codes ENT 27 738
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 1052.7 M.f. C60H78OSn2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 138-139 ºC (tech.) V.p. 8.5 ´ 10-5 mPa (extrapolated to 20 ºC) KOW logP = 5.2 Henry 1.79 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1290-1330 kg/m3 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.005 mg/l (23 ºC). In acetone 6, benzene 140, dichloromethane 380 (all in g/l, 23 ºC). Very slightly soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons and mineral oils. Stability Extremely stable to heat, light, and atmospheric oxygen. Water causes conversion of fenbutatin oxide to tris(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin hydroxide, which is reconverted to the parent compound slowly at room temperature and rapidly at 98 ºC. F.p. Not autoflammable, but tech. will explode in a dust cloud if ignited
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced in USA by Shell Chemical Co. (now Du Pont Agricultural Products) and elsewhere by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd (now BASF AG). Patents US 3657451 Manufacturers BASF; Du Pont
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of all motile stages of a wide range of phytophagous mites on pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, soft fruit, vines, bananas, cucurbits, ornamentals, and glasshouse crops. Gives long residual control. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to tangerines, tangelos, and some varieties of grapefruit. Otherwise, non-phytotoxic when used as directed. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Osadan' (Japan only) (BASF); 'Torque' (BASF); 'Vendex' (Du Pont, BASF)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Torq' (Fargro) mixtures: 'Mitedown' (+ polynactins) (Eikou Kasei)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by potentiometric non-aqueous titrimetry (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 77). Residues determined by glc with ECD or FPD of suitable derivative (Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 139; Methodensammlung Rückstandsanal. Pflanzenschutzmitteln, 1987, S24; M. Sano et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1979. 62, 764). Details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2631, mice 1450, dogs >1500 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000, rats >1000 mg/kg. Irritating to skin and severely irritating to eyes. Inhalation LC50 0.23 mg a.i. (as dust)/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 100 mg/kg diet, for dogs 15 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1992]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III EC hazard T+; R26| Xi; R36/38| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 5065 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for rainbow trout 0.27 mg a.i./l (as WP formulation). Daphnia LC50 (24 h) 0.05-0.08 mg/l. Bees Acute oral LD50 >0.1 mg/bee. Other beneficial spp. No adverse effects to a wide range of predatory and parasitic arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment In soil, it is metabolised to dihydroxy-bis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)stannane and 2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl stannonic acid, presumably ultimately forming tin oxide/hydroxide. In tests in commercial use, there was minimal movement of fenbutatin oxide or its metabolites out of the top 30 cm of soil (A. Gray et al., Pestic. Sci., 43, 295-302 (1995)). |