Fungicide
FRAC 15; cinnamic acid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name dimethomorph (BSI, draft E-ISO); diméthomorphe ((m) draft F-ISO)
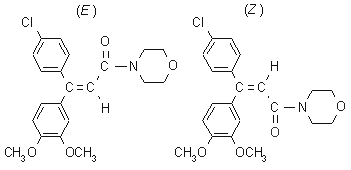
IUPAC name (E,Z)-4-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl]morpholine
Chemical Abstracts name (E,Z)-4-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]morpholine
CAS RN [110488-70-5] EEC no. 404-200-2 Development codes CME 151 (Celamerck); WL 127 294 (Shell); AC 336379 ;CL 183776; CL 336379 (all Cyanamid)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition (E)- to (Z)- ratio is c. 1:1. Mol. wt. 387.9 M.f. C21H22ClNO4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 127-148 ºC; (E)- isomer 135.7-137.5 ºC; (Z)- isomer 169.2-170.2 ºC V.p. (E)- isomer 9.7 × 10-4 mPa; (Z)- isomer 1.0 × 10-3 mPa (both 25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.63 (E)- isomer; 2.73 (Z)- isomer (both 20 ºC) S.g./density Bulk density 1318 kg/m3 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 19 (pH 5), 18 (pH 7), 16 (pH 9) (all in mg/l, 20 °C). In acetone 88 (E), 15 (Z), cyclohexanone 27 (Z), dichloromethane 315 (Z), dimethylformamide 272 (E), 40 (Z), hexane 0.04 (E), 0.02 (Z), methanol 7 (Z), toluene 7 (Z) (all in g/l, 20-23 ºC). In n-hexane 0.11, methanol 39, ethyl acetate 48.3, toluene 49.5, acetone 100, dichloromethane 461 (all for (EZ), in mg/l). Stability Hydrolytically and thermally stable under normal conditions. Stable for >5 years in the dark. The (E)- and (Z)- isomers are interconverted in sunlight.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits the formation of the oomycete fungal cell wall. Mode of action Local systemic fungicide with good protectant and antisporulant activity. Only the (Z)- isomer is intrinsically active, but, because of rapid interconversion of isomers in the light, it has no advantage over the (E)- isomer in practice. Uses Fungicide effective against Oomycetes, especially Peronosporaceae and Phytophthora spp. (but not Pythium spp.) in vines, potatoes, tomatoes and other crops. Used in combination with contact fungicides, and applied at 2.0-2.5 kg dimethomorph/ha. Formulation types DC; WG; WP.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rp hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 39-46) or capillary gc. Details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 4300, female rats 3500, male mice >5000, female mice 3700 mg/kg b.w. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg b.w. Not irritant to skin or eyes of rabbits. Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.2 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 200 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 450 mg/kg diet. Non-oncogenic in 2 y studies in rats and mice. ADI 0.09 mg/kg b.w. Other Acute i.p. LD50 for male rats 327, female rats 297 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III ('Acrobat MZ')
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 >5300 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >25, carp 14, rainbow trout 3.4 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 49 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) >20 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees at 0.1 mg/bee (contact or oral, highest dose tested). Worms EC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, the major route of metabolism is demethylation of one of the dimethoxy groups or by oxidation of one of the CH2 groups (ortho- or meta- position) of the morpholine ring. The major route of excretion was the faeces. Plants The only significant component of the residue, when present, is the parent compound. Soil/Environment Moderately mobile (Kd 2.09-11.67 ml/g, Koc 290-566). Aerobic soil metabolism DT50 66-117 d; no degradates identified except for CO2. |