Fungicide
FRAC Y; multi-site: quinone
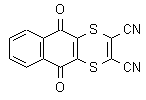
NOMENCLATURE
Common name dithianon (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, JMAF); no name (Italy)
IUPAC name 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithi-in-2,3-dicarbonitrile
CAS RN [3347-22-6] EEC no. 222-098-6 Development codes IT-931 (E. Merck); MV 119A; CME107 (Celamerck); SAG 107; CL 37114 (Cyanamid)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 296.3 M.f. C14H4N2O2S2 Form Dark brown crystals, with a coppery lustre; (tech., lighter brown). M.p. 225 ºC; (tech., c. 217 ºC) V.p. 2.7 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.2 Henry 5.71 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1576 kg/m3 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.14 mg/l (pH 7, 20 ºC). In chloroform 12, acetone 10, benzene 8 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Sparingly soluble in methanol and dichloromethane. Stability Decomposed by alkaline media, by concentrated acids, and by prolonged heating; DT50 12.2 h (pH 7, 25 ºC). Stable up to 80 ºC. Aqueous solution (0.1 mg/l) exposed to artificial sunlight had DT50 19 h. F.p. Ignition temperature >300 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by J. Berker et al. (Proc. Br. Insectic. Fungic. Conf., 2nd, 1963, p. 351). Introduced by E. Merck and later by Shell Agrar GmbH (now BASF AG). Patents GB 857383 Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Affects a range of fungal enzymes by reacting with thiol groups and interfering with cellular respiration. Multi-site mode of action. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protective and, to some extent, curative action. Uses Control of many foliar diseases (but not powdery mildews), including scab on pome fruit; Stigmina carpophila, Coccomyces hiemalis and scab on cherries; Monilia spp., rust and leaf curl on peaches and apricots; leaf spot and rust on currants; Didymella applanata on raspberries; Mycosphaerella fragariae and Diplocarpon earliana on strawberries; Plasmopara viticola on vines; downy mildew on hops; scab and Phomopsis citri on citrus fruit; Ascochyta chrysanthemi on chrysanthemums under glass; Glomerella cingulata on coffee; Marssonina leaf spot on poplars; etc. Applied at 1400 g/ha (hops), 525 g/ha (pome and stone fruit), 560 g/ha (vines). Phytotoxicity Slight russetting may occur on some apple varieties, such as Golden Delicious. Formulation types SC; WG; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with petroleum oils, alkaline materials, and sulfur-containing compounds. Selected tradenames: 'Delan' (BASF); 'Cluster' (Barclay); mixtures: 'Aktuan' (+ cymoxanil) (BASF)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Ditianroc' (Rocca)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc or by colorimetry (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2105; ibid., 1995, G, 50-55; E. Amodori & W. Heupt, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 181). Residues determined by hplc or by colorimetry (idem, ibid.). Details from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 678, guinea pigs 115 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Mild skin and eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 2.1 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 20, dogs 40 mg/kg diet; for mice 2.8 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1992]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC hazard Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male quail 430, female quail 290 mg/kg. Fish Toxic to fish; LC50 (96 h) for common carp 0.1 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) 2.4 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) 12 mg/l. Bees Contact LD50 >0.1 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (7 d) 588.4, (14 d) 578.4. Other beneficial spp. Low hazard to predatory mites.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Freundlich K 18-56 mg/kg in soils (o.c. 0.7-2.6%, pH 4.8-6.6). |