Fungicide, algicide, molluscicide
FRAC X
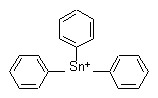
NOMENCLATURE
fentin
Common name fentin (BSI, E-ISO); fentine ((f) F-ISO); fenolovo* (former exception, USSR); chemical name is used (Republic of South Africa, USA)
IUPAC name triphenyltin
Chemical Abstracts name triphenylstannylium
CAS RN [668-34-8] Development codes VP 1940; Hoe 02824 (Hoechst)
fentin acetate
IUPAC name triphenyltin(IV) acetate; triphenyltin acetate
Chemical Abstracts name (acetyloxy)triphenylstannane
CAS RN [900-95-8] EEC no. 212-984-0 Development codes Hoe 002782 (Hoechst) Official codes OMS 1020; ENT 25208
fentin hydroxide
IUPAC name triphenyltin(IV) hydroxide; triphenyltin hydroxide
Chemical Abstracts name hydroxytriphenylstannane
CAS RN [76-87-9] EEC no. 200-990-6 Official codes OMS 1017; ENT 28009
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
fentin
Mol. wt. 350.0 M.f. C18H15Sn
fentin acetate
Composition Tech. grade is ³94% pure. Mol. wt. 409.0 M.f. C20H18O2Sn Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 121-123 ºC; (tech., 118-125 ºC) V.p. 1.9 mPa (60 ºC) KOW logP = 3.43 S.g./density 1.5 (20 ºC) Solubility In water c. 9 mg/l (20 ºC, pH 5). In ethanol 22, ethyl acetate 82, hexane 5, dichloromethane 460, toluene 89 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable when dry. Converted to fentin hydroxide in the presence of water. Unstable in acids and alkalis (22 ºC), DT50 <3 h (pH 5, 7 or 9). Decomposed by sunlight and by atmospheric oxygen.
fentin hydroxide
Composition Tech. grade is ³95% pure. Mol. wt. 367.0 M.f. C18H16OSn Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 118-120 ºC V.p. 0.047 mPa (50 ºC) KOW logP = 3.43 S.g./density 1.54 at 20 ºC Solubility In water c. 1 mg/l (pH 7, 20 ºC), (greater at lower pH values). In ethanol c. 10, dichloromethane 171, diethyl ether 28, acetone c. 50 (all in g/l, 20 ºC); in benzene 41 g (as bis(triphenyltin) oxide)/l. Stability Stable in the dark at room temperature. Dehydration occurs on heating above 45 ºC, yielding bis(triphenyltin) oxide, which is stable up to c. 250 ºC. Slowly decomposed by sunlight, and more rapidly by u.v. light, to give inorganic tin via di- and mono- phenyltin compounds.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicidal properties of organotin compounds investigated by G. J. M. van der Kerk & J. G. A. Luijten (J. Appl. Chem., 1954, 4, 314; 1956, 6, 56) and reviewed by H. Bock (Residue Rev., 1981, 79, 1). Fentin acetate was introduced by Hoechst AG (now Aventis CropScience) and fentin hydroxide by N.V. Philips-Duphar (now Uniroyal Chemical, part of CK Witco Corp.).
fentin acetate
Patents US 3499086 (Hoechst) Manufacturers Aventis
fentin hydroxide
Manufacturers Aventis
APPLICATIONS
fentin acetate
Biochemistry Multi-site inhibitor, preventing spore germination, and inhibiting metabolism of the fungal organism, in particular respiration. Mode of action Non-systemic fungicide with mainly protective action, but also some curative action. Also acts as an algicide and molluscicide. Uses Control of early and late blights of potatoes; Septoria leaf spot on celery and celeriac; leaf spot diseases of onions, sugar beet and peanuts; anthracnose of beans; rust and leaf blotch on wheat; rust on coffee; scab on pecans; Phytophthora palmivora and Monilia roreri on cocoa; Pyricularia oryzae, Pellicularia sasakii and Helminthosporium oryzae on rice; etc. Also used for control of algae and snails in rice fields, and for control of water snails in fish ponds. Phytotoxicity Vines, ornamentals, some fruits, and glasshouse crops may be injured. Formulation types WP. Compatibility Incompatible with oil emulsions and EC formulations. Selected tradenames: 'Suzu' (Nihon Nohyaku); mixtures: 'Brestan' (+ maneb) (Aventis)
fentin hydroxide
Biochemistry Multi-site inhibitor, preventing spore germination, and inhibiting metabolism of the fungal organism, in particular respiration. Mode of action Non-systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Uses Control of early and late blights of potatoes; Septoria leaf spot on celery and celeriac; leaf spot diseases of beet and peanuts; scab and other diseases of pecans; blast diseases of rice; and fungal diseases of cocoa, coffee, and soya beans. Exhibits an anti-feeding action on leaf-eating larvae, including Spodoptera spp. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed. Tomatoes and apples may be injured. Surfactants, spreaders or stickers should not be used, as this can lead to phytotoxicity. Formulation types SC; WP. Compatibility Not compatible with strongly acidic compounds. Incompatible with oils and liquid formulations. Selected tradenames: 'Brestan' (Aventis); 'Tubotin' (Aventis); 'Super-Tin' (Chiltern, Griffin); 'Suzu-H' (Nihon Nohyaku)
OTHER TRADENAMES
fentin acetate
Discontinued names: 'Fentol' * (Bayer); 'Hokko Suzu' * (Hokko); 'Radar' * (Productos OSA)
fentin hydroxide
'Brestanid' (Aventis); 'Farmatin' (Aventis); 'Duter' (BASF); 'Keytin' (Chiltern); 'MSS Flotin 480' (Mirfield) mixtures: 'Pro-Tex' (+ maneb) (Griffin); 'Timbal F' (+ tetraconazole) (Sipcam Phyteurop) Discontinued names: 'Du Ter' * (Duphar); 'Ashlade Flotin' * (Ashlade) mixtures: 'EndSpray' * (+ metoxuron) (PBI)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis: fentin acetate and hydroxide may be determined by conversion to fentin chloride, followed by rp hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 89-94), or by hydrolysis of fentin acetate to the hydroxide, which is measured by potentiometric titration (CIPAC Handbook, 1980, 1A, 1263, 1266; AOAC Methods, 1995, 979.02) or by glc of a derivative (ibid., 984.04; CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1837; Van Rossum et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 11, 227). Residues determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry of total tin (W. H. Evans et al., Analyst (London), 1979, 104, 16; T. Ferri et al., Talanta, 1989, 36, 513) or by glc of a derivative (H. H. van den Broek et al., Analyst (London), 1988, 113, 1237; Van Rossum, loc. cit.; P. G. Baker et al., Analyst (London), 1980, 105, 282).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 62, 64 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
fentin
ADI (JMPR) 0.0005 mg/kg b.w. [1991].
fentin acetate
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 140-298, guinea pigs 20, rabbits 30-50 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats c. 450, mice 350 mg/kg. Irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 0.044, female rats 0.069 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for dogs 5 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.0005 mg/kg b.w. [1991]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC hazard T+; R26| T; R24/25| Xi; R36/38| R43| N; R50, R53
fentin hydroxide
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 171, female rats 110, male mice 245, female mice 209, male guinea pigs 27.1, female guinea pigs 31.1 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 1600 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 60.3 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 2 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.0005 mg/kg b.w. [1991]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC hazard T+; R26| T; R24/25| Xi; R36/38| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
fentin acetate
Birds LD50 for quail 77.4 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 0.32 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.32-32 mg/l. Bees Formulation not toxic to bees.
fentin hydroxide
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 38.5 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for guppies 0.054, carp 0.05, golden orfe 0.11, Japanese killifish 0.072, harlequin fish 0.042 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 16.5 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
fentin
EHC 15 (WHO, 1980).
fentin acetate
EHC 15 (WHO, 1980). Soil/Environment In soil, degraded to inorganic tin via di- and mono- phenyltin compounds. Soil DT50 c. 140 d (biological degradation in agricultural loam, 1.39-1.69% o.c., pH 7.6, room temperature). |