Fungicide
FRAC Y; multi-site: phthalimide
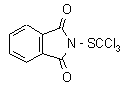
NOMENCLATURE
Common name folpet (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI, JMAF); folpel ((m) France)
IUPAC name N-(trichloromethylthio)phthalimide; N-(trichloromethanesulfenyl)phthalimide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[(trichloromethyl)thio]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
CAS RN [133-07-3] EEC no. 205-088-6
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 92-95%. Mol. wt. 296.6 M.f. C9H4Cl3NO2S Form Colourless crystals; (tech., yellow powder). M.p. 177 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 2.1 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.11 Henry 7.8 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.72 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.8 mg/l (room temperature). In carbon tetrachloride 6, toluene 26, methanol 3 (all in g/l, 25 °C). Stability Stable in the dry state. Slowly hydrolysed by moisture at room temperature. Rapidly hydrolysed in concentrated alkalis, and at elevated temperatures. F.p. Not flammable (EEC A10)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by A. R. Kittleson (Science, 1952, 115, 84). Introduced by the Standard Oil Development Co. and later by Chevron Chemical Co. Patents US 2553770; US 2553771; US 2553776 Manufacturers Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Non-specific thiol reactant, inhibiting respiration. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protective action. Uses Control of downy mildews, powdery mildews, leaf spot diseases, scab, excoriosis, black rot, white rot, Gloeosporium rots, Botrytis, Alternaria, Pythium, and Rhizoctonia spp. in pome fruit, stone fruit, soft fruit, citrus fruit, vines, olives, hops, potatoes, lettuce, cucurbits, onions, leeks, celery, tomatoes and ornamentals. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic, except to sweet cherries and the D'Anjou variety of pears. Russetting is possible in sensitive apple varieties, if applied early in cropping. Formulation types DP; SC; WG; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with strongly alkaline materials. Selected tradenames: 'Folpan' (Makhteshim-Agan, Philagro); mixtures: 'Cuprofal' (+ copper oxychloride) (Griffin); 'Fobeci' (+ benalaxyl+ cymoxanil) (Sipcam Inagra); 'Sygan PM' (+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Griffin); 'Syphal PM' (+ copper oxychloride+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Griffin)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Foldan' (Vapco); 'Verdana' (Makhteshim-Agan) mixtures: 'Altigan Flash' (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Armetil 50' (+ metalaxyl) (IQV); 'Bumper F' (+ propiconazole) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Comac' (+ copper hydroxide) (Agtrol International); 'Mikal' (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Aventis); 'Mirage Plus' (+ prochloraz) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ridomil Gold Combi' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Shavit F' (+ triadimenol) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Sirdate S' (+ cymoxanil+ oxadixyl) (Du Pont); 'Sygan LS' (+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Du Pont); 'Sygan S' (+ cymoxanil) (Du Pont); 'Syphal LS' (+ copper oxychloride+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Du Pont); 'Valiant' (+ cymoxanil+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Aventis) Discontinued names: 'Acryptan' * (Bayer); 'Phaltane' * (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectroscopy or by hplc (AOAC Methods, 1995, 977.03; CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1845). Residues determined by glc (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-I; M. A. Luke et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 1187; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 546).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >9000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >4500 mg/kg; can cause irritation of mucous membranes, contact with eyes and skin or inhalation of dust or spray mist can result in local irritation (rabbits). Skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 1.89 mg/l. NOEL In 1 y feeding trials, no ill-effect or tumour incidence was noted in albino rats receiving 800 ppm/kg diet, nor in dogs receiving 325 ppm/kg for 5 d/w. NOAEL (oncogenicity) for mice 450 ppm. No effect was observed on reproductive performance in rats over 3 generations at 1000 mg/kg diet; no teratogenic effect was noted in hamsters, monkeys or rats. ADI (JMPR) 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [1995]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV EC hazard R40| Xi; R36| R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Fish Toxic to fish. Daphnia Toxic. Algae Toxic. Other aquatic spp. Non-toxic to aquatic organisms under practical conditions because of its instability in water. Bees Non-toxic to bees; LD50 (oral) >236 mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms Non-toxic. Other beneficial spp. Slightly harmful to Coccinella septempunctata, harmless to Poecilus cupreus, Trichogramma cacoeciae, Chrysoperla carnea, Typhlodromus pyri, Aleochara bilineata and Aphidius rhopalosiphi (IOBC).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Major metabolites are phthalimide, phthalic acid and phthalamic acid. Plants As for animals. Soil/Environment DT50 (soil) 4.3 d; DT50 (water) <0.7 h. Strongly adsorbed to soil: adsorption Koc 304-1164 (calc.); unlikely to leach. |