Fungicide
FRAC 11; strobilurin type: oximinoacetate
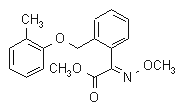
NOMENCLATURE
Common name kresoxim-methyl (BSI, pa ISO)
IUPAC name methyl (E)-methoxyimino[2-(o-tolyloxymethyl)phenyl]acetate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl (aE)-a-(methoxyimino)-2-[(2-methylphenoxy)methyl] benzeneacetate
CAS RN [143390-89-0] Development codes BAS 490F (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 313.4 M.f. C18H19NO4 Form White, mildly aromatic crystals. M.p. 98-100 °C V.p. 2.3 × 10-3 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.4 (pH 7, 25 ºC) Henry 3.6 × 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.258 kg/l (20 °C) Solubility In water 2 mg/l (20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 34 d (pH 7), 7 h (pH 9); relatively stable at pH 5. pKa None in range 2-12
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered by BASF AG in 1983. Reported by E. Ammermann et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 403). In production since 1995 and introduced in 1996. Patents EP 253213; US 4829085 Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits mitochondrial respiration by blocking electron transfer between cytochrome b and cytochrome c1, at the ubiquinol oxidising site. Selectivity is partly due to enzymic de-esterification within plants. Mode of action Fungicide with protective, curative, eradicative and long residual disease control; acts by inhibiting spore germination. Redistribution via the vapour phase contributes to activity. Uses Control of scab in apples and pears (Venturia spp.); powdery mildew on apples (Podosphaera leucotricha), vines (Uncinula necator), cucurbits (Sphaerotheca fuliginea) and sugar beet (Erysiphe betae); mildew (Erysiphe graminis), scald (Rhynchosporium secalis), net blotch (Pyrenophora teres) and glume blotch (Septoria nodorum) on cereals; mildew on vegetables (Leveillula taurica, Erysiphe spp., Alternaria spp.). Formulation types SC; SE; WG.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.6 mg/l. NOEL (3 mo) for male rats 2000 ppm (146 mg/kg daily), female rats 500 ppm (43 mg/kg daily). ADI (JMPR) 0.4 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Other Negative in the Ames test, and non-teratogenic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Although it is toxic to aquatic species, exposure tests and ecological studies have shown that there is no danger of permanent damage to aquatic organisms when kresoxim-methyl is used as recommended. Birds LD50 (14 d) for quail >2150 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.499 mg/l, rainbow trout 190 ppb. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.186 mg/l. Algae EC50 (0-72 h) 63 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (contact) >20 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >937 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Orally administered test compound was widely distributed and quickly eliminated; there was no bioaccumulation. The major routes of excretion were faeces and urine. Thirty two different metabolites were identified. Plants Residues in cereals and pome fruit at harvest are <0.05 mg/kg, in grapes and vegetables <1 mg/kg. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded; in aerobic soil, or under aerobic or anaerobic aquatic metabolism, DT50 <1 d. In soil, DT90 (lab.) <3 d; the main metabolite is the corresponding acid. Very mobile in soil; Koc 219-372; Koc of the acid 17-24. However, in lysimeter studies, only low levels of kresoxim-methyl and its metabolite were found in leachates (R. Becker-Arnold & R. T. Hamm, Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 6D-017).
|