Fungicide
FRAC Y; multi-site: alkylenebis(dithiocarbamate)
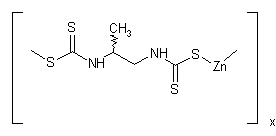
NOMENCLATURE
Common name propineb (BSI, E-ISO, JMAF); propinèbe ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name polymeric zinc propylenebis(dithiocarbamate)
Chemical Abstracts name [[(1-methyl-1,2-ethanediyl)bis[carbamodithioato]](2-)]zinc homopolymer
CAS RN [12071-83-9] monomer; [9016-72-2] (formerly [31530-30-0]) homopolymer EEC no. 235-134-0 Development codes Bayer 46 131; LH 30/Z (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 289.8 (theoretical monomer) M.f. (C5H8N2S4Zn)x Form White powder, with a slight, characteristic smell. M.p. Decomposes above 150 ºC V.p. <1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = -0.26 (PTU, main metabolite) (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.813 g/ml (23 ºC) Solubility In water 0.01 g/l (20 ºC). In toluene, hexane, dichloromethane <0.1 g/l.; in DMF + DMSO >200 g/l. Stability Stable when dry. Decomposed by moisture, and in acidic and alkaline media; DT50 (22 ºC) (est.) 1 d (pH 4), c. 1 d (pH 7), >2 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by H. Goeldner (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1963, 16, 49) and reviewed by F. Grewe (ibid., 1967, 20, 581). Introduced by Bayer AG. Patents BE 611960 Manufacturers Bayer
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Non-specific, multi-site fungicide. Mode of action Basic foliar fungicide with protective action. Conidia or germinating conidia are killed by contact. Uses Control of downy mildew, black rots, red fire disease, and grey mould on vines; scab and brown rot on apples and pears; leaf spot diseases on stone fruit; Alternaria and Phytophthora blights, downy mildew, Septoria leaf spot, and leaf mould in tomatoes; Phytophthora and Alternaria blight of potatoes; downy mildew (blue mould) on tobacco; rusts and leaf spot diseases on ornamentals; rusts, leaf spot diseases and downy mildews on vegetables. Also used on citrus fruit and berry fruit, rice and tea. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended, also in young sensitive growing stages. Formulation types DP; WG; WP. Compatibility Compatible with most other powder-formulated pesticides. Not stable when combined with alkaline materials. Selected tradenames: 'Antracol' (Bayer); mixtures: 'Positron' (+ iprovalicarb) (Bayer)
OTHER TRADENAMES
Mixtures: 'Lonacol' (+ copper oxychloride) (Argentina) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by titration with iodine, after hydrolysis and conversion of the liberated carbon disulfide to dithiocarbonate (CIPAC Proc., 1981, 2, 313). Identified colorimetrically (CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 320). Residues determined by colorimetry of a complex formed with the carbon disulfide produced on hydrolysis (Analyst (London), 1980, 105, 515; K. Vogeler, Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1967, 20, 525) or by polarography (idem, ibid.). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Not irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.7 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats 50, mice 800, dogs 1000 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.007 mg/kg b.w. [1993]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for Japanese quail >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.9, golden orfe 133 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 4.7 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (96 h) 2.7 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 (oral; 70 WP, 70 WG) >100 mg/bee. Worms LD50 (14 d) for 70 WP and 70 WG >1000 mg/kg dry substrate. Other beneficial spp. Effects on non-target insects are unlikely; only predatory mites are sensitive. Under field conditions, only moderate effects were observed.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 78 (WHO, 1988; general review of dithiocarbamates). Animals Elimination is quick; almost 91% is excreted within 48 h in the urine and faeces, and 7% with exhaled air. Plants Residues of the applied compound including its metabolite propylenethiourea (PTU) were found mainly on the plant surface. Only the metabolites propyleneurea and 4-methyl-imidazoline were taken up into the plant, in very small amounts. PTU has to be considered as a relevant residue with regard to its toxicological properties. Soil/Environment For behaviour in soil, see W. Mittelstaedt & F. Fuehr, Landwirtsch. Forsch., 1977, 30, 221. Degradation is very rapid. Propineb can be classified as not mobile in soils. |