Fungicide
FRAC 3; DMI: triazole
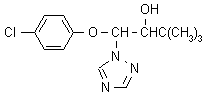
NOMENCLATURE
Common name triadimenol (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name (1RS,2RS;1RS,2SR)-1-(4-chlorophenoxy)-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
Chemical Abstracts name b-(4-chlorophenoxy)-a-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
CAS RN [55219-65-3] unstated stereochemistry; [89482-17-7] diastereoisomer A; [82200-72-4] diastereoisomer B EEC no. 259-537-6 Development codes BAY KWG 0519 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition (1RS,2SR) is referred to here as diastereoisomer A; (1RS,2RS) is referred to here as diastereoisomer B. The ratio of A:B is c. 7:3. Mol. wt. 295.8 M.f. C14H18ClN3O2 Form Colourless crystals, with a weak characteristic odour. M.p. A: 138.2 ºC; B: 133.5 ºC; eutectic A+B: 110 ºC; (tech., 103-120 ºC) V.p. A: 6 ´ 10-4 mPa; B: 4 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 °C) KOW A: logP = 3.08; B: logP = 3.28 (25 °C) Henry A: 3 ´ 10-6; B: 4 ´ 10-6 (Pa m3 mol-1, 20 °C) S.g./density A: 1.237; B: 1.299 (22 °C) Solubility In water A: 62; B: 33 mg/l (20 ºC). In dichloromethane 200-500, isopropanol 50-100, hexane 0.1-1.0, toluene 20-50 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Both diastereoisomers are stable to hydrolysis; DT50 (20 ºC) >1 y (pH 4, 7 or 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by P. E. Frohberger (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1978, 31, 11). Introduced by Bayer AG and first marketed in 1978. Patents DE 2324010 Manufacturers Bayer; Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits gibberellin and ergosterol biosynthesis and hence the rate of cell division. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective, curative and eradicant action. Absorbed by the roots and leaves, with ready translocation in young growing tissues, but less ready translocation in older, woody tissues. Uses Control of powdery mildews, rusts and Rhynchosporium in cereals, and, when applied as a seed treatment, control of bunt, smuts, Typhula spp., seedling blight, leaf stripe, net blotch and other cereal diseases. Also used on vegetables, ornamentals, coffee, hops, vines, fruit, tobacco, sugar cane, bananas and other crops, mainly against powdery mildews, rusts and various leaf spot diseases. Application rates as a spray are in the range 100-250 g/ha for bananas and cereals, 125-250 g/ha protective and 250-500 g/ha eradicative for coffee, 0.0025-0.0125% for grapes, pome and stone fruit and vegetables; application rates as a seed treatment are in the range 20-60 g/100 kg seed for cereals, 30-60 g/100 kg seed for cotton. Formulation types DP; DS; EC; EW; FS; GR; SC; WG; WP; WS. Selected tradenames: 'Bayfidan' (spray application) (Bayer); 'Noidio' (Agrimix); mixtures: 'Baytan Secur' (+ fuberidazole+ imidacloprid) (seed treatment) (Bayer); 'Baytan Spezial' (+ fuberidazole) (seed treatment) (Bayer); 'Baytan Universal' (+ fuberidazole+ imazalil) (seed treatment) (Bayer); 'Cereline Secur' (+ bitertanol+ fuberidazole+ imidacloprid) (UK) (Bayer); 'Cereline Secur' (+ fuberidazole+ imidacloprid) (seed treatment) (Bayer); 'Matador' (+ tebuconazole) (spray) (Bayer)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Repulse' (Bayer); 'Summit' (Bayer); 'Euro' (Rocca); 'Prodimenol' (Probelte); 'Shavit' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Vydan' (Vapco) mixtures: 'Abilis' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, France) (Bayer); 'Baysiston' (+ disulfoton) (Bayer); 'Baytan flowable' (+ fuberidazole) (Bayer); 'Cereline' (+ bitertanol+ fuberidazole) (Bayer); 'Coloso' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, Argentina) (Bayer); 'Domestin' (+ bitertanol+ fuberidazole) (Bayer); 'Falcon' (+ spiroxamine+ tebuconazole) (spray) (Bayer); 'Folicur Plus' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, E. Europe) (Bayer); 'Garnet' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, UK) (Bayer); 'Manta Plus' (+ fuberidazole+ imazalil+ imidacloprid) (Germany) (Bayer); 'Ruby' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, UK) (Bayer); 'Silvacur Combi' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, Central America) (Bayer); 'Silvacur' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, UK) (Bayer); 'Veto F' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, UK) (Bayer); 'Shavit F' (+ folpet) (Makhteshim-Agan) Discontinued names: 'Spinnaker' * (Cyanamid) mixtures: 'Baytan TA' * (+ anthraquinone+ triazoxide) (France) (Bayer); 'Brio Flo' * (+ anthraquinone+ triazoxide) (France) (Bayer); 'Brio' * (+ anthraquinone+ triazoxide) (France) (Bayer); 'Colt' * (+ tridemorph) (Bayer); 'Dorin' * (+ tridemorph) (Bayer); 'Folicur Bayfidan' * (+ tebuconazole) (spray, Switzerland) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by gc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 224-229). Residues determined by glc (W. Specht & M. Tillkes, Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1980, 33, 61; R. Brennecke, ibid., 1984, 37, 68; A. Allmendinger, ibid., 1991, 44, 5). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 56, 58 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 700, mice c. 1300 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.9 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 125, for dogs 600 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.05 mg/kg b.w. [1989]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC hazard (Xn; R22)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for golden orfe 17.4-27.3, rainbow trout 14-23.5, bluegill sunfish 15 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 51 mg/l. Algae ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 3.7 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida 772 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, triadimenol was metabolised mainly by oxidation of the tert-butyl moiety to the corresponding alcohol and then to carboxylic acid. A small fraction of these compounds was conjugated. Oxidation at the hydroxyl group to the corresponding keto compound (triadimefon, q.v.) and its subsequent oxidation at the tert-butyl moiety was of secondary importance. Plants The most important breakdown reactions of triadimenol in plants after seed treatment and spray application are conjugation of the a.i. with various sugar compounds (especially hexose) and oxidation at the tert-butyl moiety. The resulting primary alcohol is likewise partly conjugated. After seed treatment, the 1,2,4-triazole formed in the soil by hydrolysis was taken up into the plant via the roots and conjugated with various endogenous plant substances. Soil/Environment In soil, triadimenol is a degradation product of triadimefon (q.v.). Degradation involving hydrolytic cleavage leads to the formation of 4-chlorophenol. Metabolism of the individual triadimenol enantiomers proceeds at different rates (T. Clark et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1986, 475). DT50 in sandy loam 110-375 d; in loam 240-270 d. |