Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
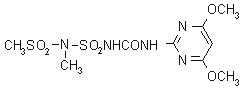
NOMENCLATURE
Common name amidosulfuron (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name 1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-mesyl(methyl)sulfamoylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-N-methylmethanesulfonamide
CAS RN [120923-37-7] Development codes AE F075032 (AgrEvo); Hoe 075032 (Hoechst)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 369.4 M.f. C9H15N5O7S2 Form White, crystalline powder. M.p. 160-163 ºC V.p. 2.2 × 10-2 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.63 (pH 2, 20 ºC) Henry 5.34 × 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.5 Solubility In water 3.3 (pH 3), 9 (pH 5.8), 13 500 (pH 10) mg/l (20 ºC). In isopropanol 0.099, methanol 0.872, acetone 8.1 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable for 2 years at 25 ºC in unopened original containers. Abiotic hydrolysis, DT50 33.9 d (pH 5), 365 d (pH 7), 365 d (pH 9) (25 ºC). pKa 3.58
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Selective, systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots and translocated throughout the plant. Plant growth is inhibited, followed by the development of chlorotic patches which spread acropetally and then basipetally. Uses Post-emergence control of a wide range of broad-leaved weeds, especially cleavers, in winter wheat, durum wheat, barley, rye, triticale and oats, at 30-60 g/ha; controls docks in pasture. Formulation types WG. Selected tradenames: 'Gratil' (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
By reverse phase hplc. Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707). Details available from Aventis.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.8 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 400 ppm diet (19.45 mg/kg b.w. daily). ADI 0.2 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-teratogenic and non-mutagenic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >320 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 36 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 47 mg/l. Bees Acute oral LD50 >1000 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The major metabolic pathway in the rat is O-demethylation. Soil/Environment In soil, amidosulfuron is degraded microbially, DT50 3-29 d. Degradation is independent of the pH value, but dependent on the biological activity in the soil.
|