Herbicide
HRAC O WSSA 4; pyridinecarboxylic acid
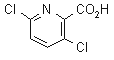
NOMENCLATURE
clopyralid
Common name clopyralid (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO); 3,6-dichloropicolinic acid (WSSA, Canada, Finland and, until 1984, BSI; name accepted in lieu of a common name); acide dichloro-3,6 picolinique (France and, until 1984, F-ISO; name accepted in lieu of a common name)
IUPAC name 3,6-dichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 3,6-dichloro-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid
Other names 3,6-DCP CAS RN [1702-17-6] EEC no. 216-935-4 Development codes Dowco 290 (Dow)
clopyralid-olamine
Common name clopyralid-olamine
CAS RN [57754-85-5]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
clopyralid
Mol. wt. 192.0 M.f. C6H3Cl2NO2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 151-152 ºC V.p. 1.33 mPa (pure, 24 ºC); 1.36 mPa (tech., 25 ºC) KOW logP = -1.81 (pH 5), -2.63 (pH 7), -2.55 (pH 9), 1.07 (unionised, 25 °C) S.g./density 1.57 (20 ºC) Solubility Pure (99.2%) 7.85 (in distilled water), 118 (pH 5), 143 (pH 7), 157 (pH 9) (all in g/l, 20 ºC). In acetonitrile 121, n-hexane 6, methanol 104 (all in g/kg). Forms water-soluble salts, for example potassium, solubility >300 g/l (25 ºC). Stability Decomposes above m.p. Stable in acidic media and to light; on hydrolysis, DT50 >30 d at pH range 5-9 (25 ºC) in sterile water. pKa 2 F.p. No flashing exhibited in ignition test
clopyralid-olamine
Mol. wt. 253.1 M.f. C8H10Cl2N2O3 Solubility In water 560 g/l (25 ºC).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by T. Haagsma (Down Earth, 1975, 30(4), 1). Introduced in France (1977) by Dow Chemical Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). Patents US 3317549
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation both acropetally and basipetally, and accumulation in meristematic tissue. Exhibits an auxin-type reaction. Acts on cell elongation and respiration.
clopyralid
Uses Post-emergence control of many annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds of the families Polygonaceae, Compositae, Leguminosae, and Umbelliferae, in sugar beet, fodder beet, oilseed rape, maize, brassicas, onions, leeks, strawberries, flax and grassland. Provides particularly good control of creeping thistle (Cirsium arvense), perennial sow-thistle, coltsfoot, mayweeds, and Polygonum spp. Phytotoxicity Good crop tolerance of graminaceous, cruciferous crops. Formulation types SL. Selected tradenames: 'Clio' (Agriphar); 'Cyronal' (Aventis); 'Diclopyr' (Agrimix); mixtures: 'Scorpion' (+ benazolin+ dimefuron) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc. Residues determined by glc of a derivative (A. J. Pik & G. W. Hodgson, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1976, 59, 264). Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
clopyralid
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3738, female rats 2675 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg; a severe eye irritant, not a skin irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.38 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 15, male mice 500, female mice >2000 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.15 mg/kg. Other Non-carcinogenic, non-mutagenic, non-teratogenic, and produces no significant toxicological effects on reproductive parameters. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV EC hazard Xi; R41| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
clopyralid
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 1465, bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >4640 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 103.5, bluegill sunfish 125.4 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 225 mg/l. EC50 (21 d) immobilisation 69, reproduction 80 mg/l; NOEC 17 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum, cell count 6.9, cell volume 7.3 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 89 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees. LD50 (48 h, oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. No effect on nitrification, nitrogen fixation or degradation of cellulose, starch, protein and leaf material at 1-10 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, there is rapid and almost quantitative unchanged elimination in the urine. Plants Clopyralid is not metabolised in plants. Soil/Environment In soil, microbial degradation occurs; slow degradation occurs in sterile soil. The major product is CO2; only traces of one other metabolite have been recorded. Aerobic soil degradation depends on initial concentration (DT50 range 7 at 0.0025 ppm to 435 at 2.5 ppm, sandy loam), soil temperature and soil moisture; DT50 (BBA guidelines) 14-56 d; DT50 (USA guidelines) 2-94 d. Mean Koc 4.64 (range 0.4-12.9), mean Kd 0.0412 (range 0.0094-0.0935); when aged in loam soil for 30 d, Koc was c. 30 ml/g, suggesting clopyralid would be more tightly sorbed. Although data indicate potential for leaching, field dissipation and lysimeter studies demonstrate fairly rapid degradation and limited downward movement. Field dissipation DT50 was 8-66 d (19 sites), with downward movement confined to 18 in. In lysimeter studies, the centre of mass movement ranged from 6-18 in. after 12 months, and cumulative (2 y) leachate concentrations were 0.002-0.14 ppb (0.1-0.6% of applied).
|