Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; bis-carbamate
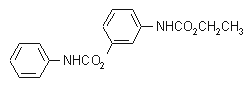
NOMENCLATURE
Common name desmedipham (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); desmédiphame ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name ethyl 3-phenylcarbamoyloxyphenylcarbamate; ethyl 3'-phenylcarbamoyloxycarbanilate; 3-ethoxycarbonylaminophenyl phenylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl [3-[[(phenylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]carbamate
Other names DMP CAS RN [13684-56-5] Development codes SN 38 107 (Schering); ZK 14 494; EP 475
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is c. 97.5% pure. Mol. wt. 300.3 M.f. C16H16N2O4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 120 ºC V.p. 4× 10-5 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.39 (pH 5.9) S.g./density Pour 0.536, tap 0.620 Solubility In water 7 mg/l (pH 7, 20 ºC). Readily soluble in polar organic solvents, e.g. acetone 400, isophorone 400, methanol 180, ethyl acetate 149, chloroform 80, dichloroethane 17.8, benzene 1.6, toluene 1.2, hexane 0.5 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in aqueous acidic media, but hydrolysed in neutral and alkaline media. Stable for 2 years at 70 ºC; DT50 224 h in aq. solution at pH 3.8 exposed to light ≥ 280 nm; on hydrolysis, DT50 c. 70 d at pH 5, c. 20 h at pH 7, 10 min at pH 9.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed through the leaves, with translocation primarily in the apoplast. Uses Used post-emergence to control broad-leaved weeds, including Amaranthus retroflexus, in beet crops, in particular sugar beet. Usually sprayed in combination with phenmedipham and ethofumesate. Desmedipham acts through the leaves only, and does not depend on soil type and humidity under normal growing conditions. Due to its wide safety margin to the crop, spraying is merely timed according to the development stage of the weeds, with optimum weed control when they are at the cotyledon stage. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to beet crops. Formulation types EC; SC. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline substances.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc or colorimetry of a derivative. Residues determined by hydrolysis to aniline using derivatives suitable for glc (C.-H. Roeder et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 293) or hplc. Details available from Aventis.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >10 250, mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >4000 mg/kg. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >7.4 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 3.2 mg/kg daily, for mice 22 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.00125 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (14 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.7, bluegill sunfish 3.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.88 mg/l. Algae IC50 (72 h) 0.061 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 >50 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 466.5 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 80% of the parent compound and its metabolites are eliminated in the urine within 24 hours. Hydrolysis to ethyl N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)carbamate (EHPC) and conjugation (to glucuronides and ethereal sulfates) are the major steps in metabolism. Plants In sugar beet, EHPC is the major metabolite, with m-aminophenol as a further metabolite. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil c. 34 d, DT90 <115 d, with formation of ethyl 3-hydroxycarbanilate, which undergoes further degradation. Therefore, desmedipham does not accumulate in soil, nor is there any relevant uptake by following crops. Due to its favourable physico-chemical parameters, there is no risk of groundwater contamination to be expected. Koc 1500. |