Herbicide
HRAC C2 WSSA 7; urea
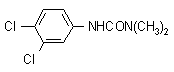
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); DCMU (JMAF); dichlorfenidim* (former exception, USSR)
IUPAC name 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethylurea
CAS RN [330-54-1] EEC no. 206-354-4 Development codes DPX 14740 (Du Pont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 233.1 M.f. C9H10Cl2N2O Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 158-159 ºC V.p. 1.1 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.85?.03 (25 ºC) Henry 7.04 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.48 Solubility In water 36.4 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 53, butyl stearate 1.4, benzene 1.2 (all in g/kg, 27 ºC). Sparingly soluble in hydrocarbons. Stability Stable in neutral media at normal temperatures, but hydrolysed at elevated temperatures. Hydrolysed by acids and alkalis. Decomposes at 180-190 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. C. Bucha & C. W. Todd (Science, 1951, 114, 493). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents US 2655445 Manufacturers Ancom; Aventis; Bayer; Cedar; Crystal; Defensa; Drexel; ÉMV; Griffin; Hegang Heyou; Hodogaya; Makhteshim-Agan; Nufarm Ltd; Sanachem; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Systemic herbicide, absorbed principally by the roots, with translocation acropetally in the xylem. Uses Total control of weeds and mosses on non-crop areas, at 10-30 kg a.i./ha. Selective control of germinating grass and broad-leaved weeds in many crops, including asparagus, tree fruit, bush fruit, citrus fruit, vines, olives, pineapples, bananas, sugar cane, cotton, peppermint, alfalfa, forage legumes, cereals, maize, sorghum, and perennial grass-seed crops, at 0.6-4.8 kg/ha. Phytotoxic residues in soil disappear within 1 season at these lower rates. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Direx' (Griffin); 'Karmex' (Griffin); 'Cekuron' (Cequisa); 'Diurex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Dynex' (Crystal, Cedar); 'Inquiron' (Inquiport); 'Sadiuron' (ÉMV); 'Sanuron' (Sanachem); 'Seduron' (Aventis); 'Unidron' (Unicrop); mixtures: 'Rapir Neu' (+ amitrole) (Bayer)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Baron' (Chemiplant); 'Cañex' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Cention' (Aventis); 'Crisuron' (Crystal); 'Monex' (Ancom); 'Sanduron' (Sanachem); 'Toterbane' (Diachem); 'Vidiu' (Vipesco) mixtures: 'Krovar' (+ bromacil) (Du Pont); 'Amigo' (+ amitrole) (CFPI Nufarm); 'Anuron' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Ancom); 'Cottonex D' (+ fluometuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Crisquat D' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Crystal); 'Dexuron' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Nomix-Chipman); 'Dirimal' (+ oryzalin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Diumate' (+ MSMA) (Drexel); 'Dropp Ultra' (+ thidiazuron) (Aventis); 'Duopan' (+ oryzalin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Ginstar' (+ thidiazuron) (Aventis); 'Gramocil' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Syngenta); 'Herboxone D' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Crystal); 'Kytrol G' (+ amitrole+ bromacil) (CFPI Nufarm); 'Nomix TH 20' (+ glyphosate) (Monsanto); 'Pardy' (+ paraquat dichloride) (Agricultura Nacional); 'Sahara' (+ imazapyr) (BASF); 'Topsite' (+ imazapyr) (BASF); 'Touch? (+ glyphosate) (Nomix-Chipman); 'Trevissimo' (+ glyphosate) (Calliope); 'Trik' (+ 2,4-D+ amitrole) (Mirfield); 'Uracom' (+ amitrole) (Luxan); 'Ustinex G' (+ glyphosate) (Bayer); 'Xanadu' (+ glyphosate) (Monsanto) Discontinued names: 'Dion' * (Makhteshim-Agan) mixtures: 'Novorail' * (+ amitrole+ ethidimuron) (CFPI)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (G. W. Sheehan, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 227), or by hydrolysis and titration of the amine liberated (CIPAC Handbook, 1980, 1A, 1251), details available from Du Pont. Impurities by tlc (ibid., 1994, F, 336). Residues determined by glc (Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 664; W. E. Bleidner, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1954, 2, 682). Hydrolysis to 3,4-dichloroaniline, a derivative of which is measured colorimetrically, may also be used (H. L. Pease, ibid., 1962, 10, 279; R. L. Dalton & H. L. Pease, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1962, 45, 377). In water, by lc with u.v. detection (AOAC Methods, 1995, 992.14, 10.7.01).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 3400 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg for 80% DF. Mild eye irritant (WP formulation) (rabbits); non-irritating to intact skin (50% aqueous paste) (guinea pigs). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 250, dogs 125 mg/kg diet (H. C. Hodge et al., Food Cosmet. Toxicol., 1967, 5, 513). ADI (EPA) 0.002 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III EC hazard R40| R40| Xn; R22, R48/22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 1730, Japanese quail >5000, mallard ducklings >5000, pheasant chicks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 5.6, bluegill sunfish 5.9, guppies 25 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 12 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, metabolism is principally by hydroxylation and dealkylation (C. Boehme & W. Ernst, Food Cosmet. Toxicol., 1965, 3, 797-802). Plants In plants, diuron undergoes demethylation of the nitrogen atom and hydroxylation at position 2 of the benzene ring. Soil/Environment In soil, enzymic and microbial demethylation of the nitrogen atom and hydroxylation at position 2 of the benzene ring occur. Duration of activity in soil is c. 4-8 mo, depending on soil type and humidity; DT50 90-180 d (G. D. Hill et al., Agron. J., 1955, 47, 93; T. J. Sheets, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1964, 12, 30). Koc 400. |