Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; aryloxyphenoxypropionate
NOMENCLATURE
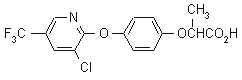
haloxyfop
Common name haloxyfop (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, WSSA)
IUPAC name (RS)-2-[4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)phenoxy]propionic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (-2-[4-[[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenoxy]propanoic acid
CAS RN [69806-34-4] unstated stereochemistry; [95905-78-5] racemate Development codes DOWCO 453 (Dow)
haloxyfop-etotyl
IUPAC name ethoxyethyl (RS)-2-[4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)phenoxy]propionate
Chemical Abstracts name 2-ethoxyethyl (-2-[4-[[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenoxy]propanoate
CAS RN [87237-48-7] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 402-560-5 Development codes DOWCO 453 EE (Dow)
haloxyfop-P-methyl
IUPAC name methyl (R)-2-[4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)phenoxy]propionate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl (R)-(+)-2-[4-[[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenoxy]propanoate
Other names haloxyfop-R (methyl ester) CAS RN [72619-32-0]; acid [95977-29-0] EEC no. 406-250-0 Development codes DE-535 (Dow)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
haloxyfop
Mol. wt. 361.7 M.f. C15H11ClF3NO4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 107-108 ºC V.p. <1.33 × 10-3 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.34 (20 ºC, unstated pH) S.g./density 1.64 Solubility In water 43.4 mg/l (pH 2.6, 25 ºC); 1.590 (pH 5), 6.980 (pH 9) (both in mg/l, 20 ºC). In acetone, methanol, isopropanol >1000, dichloromethane 459, ethyl acetate 518, toluene 118, xylene 74, hexane 0.17 (all in g/l). Stability DT50 in water 78 d (pH 5), 73 d (pH 7), 51 d (pH 9). pKa 2.9
haloxyfop-etotyl
Mol. wt. 433.8 M.f. C19H19ClF3NO5 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 58-61 ºC V.p. 1.64 ×10-5 mPa (20 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 4.33 (20 ºC) (OECD 107) S.g./density 1.34 Solubility In water 0.58 (unbuffered), 1.91 (pH 5), 1.28 (pH 9.2) (all in mg/l, 20 ºC). In dichloromethane 2760, xylene 1250, acetone, ethyl acetate, toluene >1000, methanol 233, isopropanol 52, hexane 44 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysed to haloxyfop under acidic and alkaline conditions. In water, DT50 33 d (pH 5), 5 d (pH 7), a few h (pH 9) (all 25 ºC).
haloxyfop-P
Mol. wt. 361.7 M.f. C15H11ClF3NO4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 70.5-74.5 °C V.p. 3.5 × 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.27 (pH 7) Solubility In water 375 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone, dichloromethane, methanol, xylene >639 g/l (20 ºC). pKa 4.27
haloxyfop-P-methyl
Composition The (R)- isomer of haloxyfop-methyl. Mol. wt. 375.7 M.f. C16H13ClF3NO4 Form Clear brown, odourless liquid. B.p. >280 ºC V.p. 0.328 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.00 Henry 1.1 × 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.372 (20 °C) Solubility In water 9.08 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, cyclohexanone, dichloromethane, ethanol, methanol, toluene, xylene >1 kg/l (20 ºC). Stability DT50 in water 100 d (pH5), 48 d (pH7), 52 h (pH9) (all 25°C). F.p. 186 °C
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Mode of action Haloxyfop-etotyl and haloxyfop-P-methyl are selective herbicides, absorbed by the foliage and roots, and hydrolysed to haloxyfop, which is translocated to meristematic tissues, and inhibits their growth. Uses Haloxyfop-etotyl and haloxyfop-P-methyl are used post-emergence for control of annual and perennial grasses in sugar beet, fodder beet, oilseed rape, potatoes, leaf vegetables, onions, flax, sunflowers, soya beans, vines, strawberries, and other crops. Applied at 104-208 g a.e./ha (-etotyl) and 52-104 g a.e./ha (-P-methyl). Formulation types EC. Compatibility Compatible with many other grass herbicides, and with post-emergence broad-leaved herbicides.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of haloxyfop-etotyl and haloxyfop-P-methyl by hplc. Residues determined by glc. Details available from Dow AgroSciences
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
haloxyfop
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 337 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.065 mg/kg daily; no increase in hepatotoxicity. ADI (JMPR) 0.0003 mg/kg b.w. [1995]; (Germany) 0.00065 mg/kg b.w. [1997]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II
haloxyfop-etotyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 531, female rats 518 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin; moderate eye irritant (rabbits). No sensitisation (guinea pigs). NOEL for rats 0.065 mg/kg daily. ADI As haloxyfop. EC hazard Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
haloxyfop-P-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 300, female rats 623 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin; slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.065 mg/kg daily; no increase in hepatotoxicity. ADI As haloxyfop.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
haloxyfop
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout >800 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 96.4 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) 106.5 mg/l.
haloxyfop-etotyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for fathead minnows 0.54, bluegill sunfish 0.28, rainbow trout 1.18 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 4.64 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact and oral) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 880 mg/kg.
haloxyfop-P
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 414 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >50 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) >70 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, oral and contact) >100 mg/bee.
haloxyfop-P-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1159 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.7 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 6.12 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) 1.72 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 1343 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
haloxyfop-etotyl
Animals In mammalian systems, haloxyfop-etotyl is rapidly hydrolysed to the parent acid haloxyfop, converted to the R- enantiomer, and eliminated. Plants Hydrolysed to haloxyfop, terminal residue haloxyfop or conjugates. Soil/Environment In soil, haloxyfop-etotyl is converted to haloxyfop. DT50 <1 d on silty clay loam (20 ºC). Adsorption in silty clay loam soil (pH 7.0, 1.97% o.c.) Koc 128. Haloxyfop acid degradation approximates to a first order kinetic process and involves degradation to the pyridinol and other minor metabolites; DT50 27 - 100 d, average 55 d (various soil types).
haloxyfop-P-methyl
Animals In mammals, haloxyfop-methyl (R)- isomer is rapidly converted to the parent acid and eliminated. Plants Hydrolysed to haloxyfop, terminal residue haloxyfop, or conjugates. Soil/Environment DT50 <24 h, forming the parent acid, which is then microbially degraded. Haloxyfop acid degradation approximates to second or square root first order kinetics and involves degradation to the pyridinol and other minor metabolites. DT50 9 to 20.5 d, average 14 d (various soil types).
|