Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; imidazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
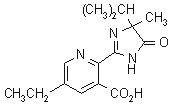
imazethapyr
Common name imazethapyr (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name (RS)-5-ethyl-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)nicotinic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (-2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-ethyl-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [81335-77-5] Development codes AC 263 499; CL 263 499 (both Cyanamid)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
imazethapyr
Mol. wt. 289.3 M.f. C15H19N3O3 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 169-173 ºC B.p. Decomp. 180 °C V.p. <0.013 mPa (60 ºC) KOW logP = 1.04 (pH 5), 1.49 (pH 7), 1.20 (pH 9) (all 25 ºC) S.g./density 1.10-1.12 (21 °C) Solubility In water 1.4 g/l (25 ºC). In acetone 48.2, methanol 105, toluene 5, dichloromethane 185, dimethyl sulfoxide 422, isopropanol 17, heptane 0.9 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Rapidly degraded in sunlight, DT50 c. 3 d. pKa pKa1 2.1, pKa2 3.9
imazethapyr-ammonium
Mol. wt. 306.4 M.f. C15H22N4O3
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Hence reduces levels of valine, leucine and isoleucine, leading to disruption of protein and DNA synthesis. Selectivity in soya benas and peanuts is attributed to rapid detoxification via hydroxylation and glycosylation (B. Tecle et al., Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 605). Mode of action Systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage, with translocation in the xylem and phloem, and accumulation in the meristematic regions. Uses Control of many major annual and perennial grass and broad-leaved weeds in soya beans and other leguminous crops. Applied pre-plant incorporated, pre-emergence, or post-emergence. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to soya beans and other leguminous crops, when used as directed. Formulation types SL.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats, and female mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg; mild skin and reversible eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 for rats 3.27 mg/l air (analytical), 4.21 mg/l (gravimetric). NOEL (2 y) for rats >10 000 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs >10 000 mg/kg diet (highest dose tested). Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
imazethapyr
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 420, rainbow trout 340, channel catfish 240 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) <1000 mg/l. Algae NOEL for Selenastrum capricornutum 50 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. I50 for Lemna gibba 4.38 mg/l. Bees Topical LD50 for honeybees >0.1 mg/bee. Worms I50 >10 000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 92% was excreted in the urine and 5% in the faeces within 24 hours. Residue levels in blood, liver, kidney, muscle, and fat tissues were <0.01 ppm after 48 hours. Plants Rapidly metabolised in non-susceptible plants; half-life in soya beans 1.6 days. The primary metabolic route in maize is oxidative hydroxylation at the a-carbon atom of the ethyl substituent on the pyridine ring. Soil/Environment Half-life in soil 1-3 months.
|