Herbicide
HRAC C2 WSSA 7; urea
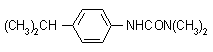
NOMENCLATURE
Common name isoproturon (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 3-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea; 3-p-cumenyl-1,1-dimethylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N,N-dimethyl-N'-[4-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]urea
Other names IPU; ipuron* CAS RN [34123-59-6] EEC no. 251-835-4 Development codes Hoe 16410 (Hoechst); AE F016410 (AgrEvo); CGA 18 731 (Ciba-Geigy); 35689 RP; LS 6912999 (Rhône-Poulenc)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³98.5% pure. Mol. wt. 206.3 M.f. C12H18N2O Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 158 ºC; (tech., 153-156 °C) V.p. 3.15 ´ 10-3 mPa (20 °C); 8.1 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 2.5 (20 ºC) Henry 1.46 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.2 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 65 mg/l (22 ºC). In methanol 75, dichloromethane 63, acetone 38, benzene 5, xylol 4, n-hexane c. 0.2 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Very stable to light, acids, and alkalis. Hydrolytically cleaved by strong alkalis on heating.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (became Novartis Crop Protection AG, who ceased to manufacture or market it), Hoechst AG and Rhône-Poulenc Agrochimie (both now Aventis CropScience). Patents GB 1407587 to Ciba-Geigy Manufacturers Atul; Aventis; ÉMV; Gharda; Griffin; Jiangsu; Makhteshim-Agan; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and leaves, with translocation. Uses Pre- and post-emergence control of annual grasses (Alopecurus myosuroides, Apera spica-venti, Avena fatua and Poa annua) and many annual broad-leaved weeds in spring and winter wheat (except durum wheat), spring and winter barley, winter rye, and triticale, at 1.0-1.5 kg a.i./ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to cereals, except durum wheats. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Alon' (Aventis); 'Arelon' (Aventis); 'Strong' (Aventis); 'Tolkan' (Aventis); 'Cordelia' (Griffin); 'Dhanulon' (Dhanuka); 'Guideline' (Barclay); 'Hilproturon' (Hindustan); 'Iprofile' (Mirfield); 'Isoguard' (Gharda); 'Narilon' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Panron' (Sanonda); 'Pasport' (RPG); 'Protugan' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Turonex' (Agriphar); mixtures: 'Javelin' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Affinity' (+ carfentrazone-ethyl) (FMC); 'Herbaflex' (+ beflubutamid) (Staehler, Ube)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Atum ' (Aventis); 'Belgran' (Aventis); 'IP Flo' (Aventis); 'Atlas Fieldgard' (Atlas Crop Protection); 'Avanon' (Gharda); 'Barclay Guideline' (Barclay); 'Bison' (Gharda); 'Isoclon' (BEC); 'Isopar' (Parry); 'Mysen' (Portman); 'Portman Isotop' (Portman); 'Proturon' (Agrochem); 'Pugil' (Tripart); 'Totalon' (Crop Health); 'Tripart Pugil' (Tripart) mixtures: 'Agrilon' (+ amidosulfuron) (Aventis); 'Autumn Kite' (+ trifluralin) (Aventis); 'Azur' (+ diflufenican+ ioxynil) (Aventis); 'Competitor' (+ fluoroglycofen-ethyl) (Aventis); 'Cougar' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Fenikan' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Grenadier' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Grodyl Plus' (+ amidosulfuron) (Aventis); 'Harlequin' (+ simazine) (Syngenta); 'Ingot' (+ diflufenican+ flurtamone) (Aventis); 'Javelin Gold' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Keos' (+ triasulfuron) (Syngenta); 'Kuorum' (+ fluoroglycofen-ethyl) (Aventis); 'Panther' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Puma Extra' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (Aventis); 'Puma X' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (Aventis); 'Quartz' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Tolkan Turbo' (+ diflufenican) (Aventis); 'Encore' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Jolt' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Landgold DFF 625' (+ diflufenican) (Landgold); 'Trump' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF) Discontinued names: 'Auger' * (Rhône-Poulenc); 'IP50' * (Rhône-Poulenc); 'MSS Iprofile' * (Mirfield); 'Sabre' * (AgrEvo) mixtures: 'Ovation' * (+ flupoxam) (Synexus); 'Stefes Competitor' * (+ fluoroglycofen-ethyl) (Stefes)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 110-115; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1982, 12) or by titration of the dimethylamine liberated on hydrolysis. Residues determined by glc (Man. Pestic. Anal. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, 1978, 1, 241; Anal. Methods of Pesticide Residues in Foodstuffs, General Inspectorate for Health Protection, Netherlands, June 1996).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1826-2417, mice 3350 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.95 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 400, dogs 50 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for rats 80 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.0062 mg/kg b.w. Water GV 9 mg/l (TDI 3 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III EC hazard R40| Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 3042-7926, pigeons >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for golden orfe 129, bluegill sunfish >100, guppies 90, rainbow trout 37, carp 193, catfish 9 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 507 mg/l. Algae LC50 (72 h) 0.03 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 (48 h, oral) >50->100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg dry artificial soil. Other beneficial spp. A dose of up to 1.5 kg/ha (as 'Arelon') was harmless to adult female Aleochara bilineata.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 50% is eliminated within the first 8 h, predominantly in the urine. Plants In plants, degradation is mainly via hydroxylation of the isopropyl group to 1,1-dimethyl-3-[4-(2'-hydroxy-2'-propyl)phenyl]urea; N-dealkylation also occurs. Soil/Environment Undergoes enzymic and microbial demethylation at the nitrogen, and hydrolysis of the phenylurea to 4-isopropylaniline. DT50 in soil 6-28 d; rate of degradation increases 3x between 10 ºC and 30 ºC (sandy soil) and 10x in an organic soil over the same temperature range. |