Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; diphenyl ether
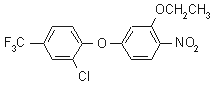
NOMENCLATURE
Common name oxyfluorfen (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); oxyfluorfène ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyl 3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenyl ether
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-1-(3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene
CAS RN [42874-03-3] EEC no. 255-983-0 Development codes RH-2915 (Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 361.7 M.f. C15H11ClF3NO4 Form Orange, crystalline solid. M.p. 85-90 ºC; (tech., 65-84 ºC) B.p. 358.2 ºC (decomp.) V.p. (pure a.i.) 0.0267 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.47 S.g./density 1.35 (73 ºC) Solubility In water 0.116 mg/l (25 ºC). Readily soluble in most organic solvents, e.g. acetone 72.5, cyclohexanone, isophorone 61.5, dimethylformamide >50, chloroform 50-55, mesityl oxide 40-50 (all in g/100 g, 25 ºC). Stability No significant hydrolysis in 28 d at pH 5-9 (25 ºC). Decomposed rapidly by u.v. irradiation; DT50 3 d (room temperature). Stable up to 50 ºC.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective contact herbicide, absorbed more readily by the foliage (and especially the shoots) than by the roots, with very little translocation. Uses Control of annual broad-leaved weeds and grasses in a variety of tropical and subtropical crops, by pre- or post-emergence application at rates in the range 0.25-2.0 kg a.i./ha. Particular crops include tree fruit (including citrus), vines, nuts, cereals, maize, soya beans, peanuts, rice, cotton, bananas, peppermint, onions, garlic, ornamental trees and shrubs, and conifer seedbeds. Phytotoxicity Soya beans and cotton may be injured by contact with oxyfluorfen. Formulation types EC; GR.
ANALYSIS
Product and residues determined by glc (I. Adler & C. K. Hoffman, Anal. Methods. Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 11, 331-341).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and dogs >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >10 000 mg/kg. Mild to moderate eye irritant; mild skin irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 >5.4 mg/l. NOEL In chronic dietary trials, NOEL for rats 40, dogs 100, mice 2 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.003 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute LD50 for bobwhite quail >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.2, trout 0.41, channel catfish 0.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.5 mg a.i./l. Bees Not toxic to honeybees at 0.025 mg a.i./bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals For details of metabolism, see I. L. Adler et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1977, 25, 1339. Plants Not readily metabolised in plants. Soil/Environment Strongly adsorbed on soil, not readily desorbed, and shows negligible leaching. Koc from 2891 (sand) to 32 381 (silty clay loam). Photodecomposition in water is rapid, and on soil is slow. Microbial degradation is not a major factor. Field dissipation DT50 5-55 d; soil DT50 (in dark) (aerobic) 292 d, (anaerobic) c. 580 d. |