Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name prometryn (BSI from 1984, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); prometryne ((f) F-ISO, JMAF and, until 1984, BSI)
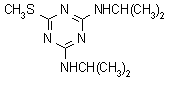
IUPAC name N2,N4-di-isopropyl-6-methylthio-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name N,N'-bis(1-methylethyl)-6-(methylthio)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [7287-19-6] EEC no. 230-711-3 Development codes G 34 161 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 97% pure. Mol. wt. 241.4 M.f. C10H19N5S Form White powder. M.p. 118-120 ºC B.p. >300 °C/100 kPa V.p. 0.165 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 3.1 (25 ºC, unionised) Henry 1.2 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.15 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 33 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 300, ethanol 140, hexane 6.3, toluene 200, n-octanol 110 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at 20 ºC in neutral, slightly acidic or slightly alkaline media. Hydrolysed by warm acids and alkalis. Decomposed by u.v. irradiation. pKa 4.1, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. Gysin (Chem. Ind. (London), 1962, p. 1393). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents CH 337019; GB 814948 Manufacturers Griffin; Makhteshim-Agan; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Also inhibits oxidative phosphorylation. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally through the xylem from the roots and foliage, and accumulation in the apical meristems. Uses Used pre-emergence, at 0.8-2.5 kg/ha, in cotton, sunflowers, peanuts, potatoes, carrots, peas and beans; post-emergence, at 0.8-1.5 kg/ha, in cotton, potatoes, carrots, celery and leeks. Phytotoxicity Used as a directed spray on cotton while young, to avoid foliar injury. Formulation types FW; SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Caparol' (USA) (Syngenta); 'Gesagard' (Syngenta); 'Cotton-Pro' (Griffin); 'Efmetryn' (Efthymiadis); 'Prometrex' (Makhteshim-Agan); mixtures: 'Cotralin' (+ alachlor) (Efthymiadis)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Primatol Z' (Syngenta); 'Agrogard' (AgroSan); 'Azogard' (Azot); 'Cottotryn' (Papaeconomou) mixtures: 'Codal' (+ ametryn) (Syngenta); 'Bandit' (+ fluometuron) (Incitec) (Crop Care); 'Cottonex P' (+ fluometuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cowark' (+ trifluralin) (Shionogi); 'Lanten' (+ terbutryn) (Aragonesas); 'Zeazin Mix DKV' (+ atrazine) (Istrochem); 'Zeazin Mix Extra' (+ atrazine+ metolachlor) (Istrochem)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1980, 1A, 1328; AOAC Methods, 1995, 971.08; R. T. Murphy et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1971, 54, 703). Residues determined by glc with ECD or FID (K. Ramsteiner et al., ibid., 1974, 57, 192; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 680; B. G. Tweedy & R. A. Kahrs, ibid., 1978, 10, 493).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3100, rabbits >2020 mg/kg. Not irritant to skin and slightly irritant to eyes of rabbits. Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5170 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats 750, dogs 150 ppm; (21 mo) for mice 10 ppm. ADI 0.01 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III (80 WP), II (4 L)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail >5000, mallard ducks >500 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 5.5, bluegill sunfish 7.9 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 12.66 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.023 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 1.7 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees. LD50 (oral) >99 mg/bee; (contact) >130 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 153 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals For metabolism in rats and rabbits, see C. Boehme & F. Baer, Food Cosmet. Toxicol., 1967, 5, 23. Plants Metabolised by tolerant plants, and, to a lesser extent, by sensitive plants, by oxidation of the methylthio group to hydroxy metabolites, and by dealkylation of the side-chains. Degradation in plants is generally slow. Soil/Environment In soil, microbial degradation takes place, with oxidation of the methylthio group to hydroxy metabolites, and dealkylation of the side-chains. Median DT50 in soil 50 d (14-158 d). Koc 400, indicating low mobility in soil. Degradation in aquatic systems is caused by microbial processes; further dissipation results from adsorption to the suspended and bottom sediments. |