Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; benzamide (mi)
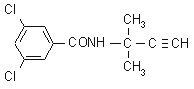
NOMENCLATURE
Common name propyzamide (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, JMAF); pronamide (WSSA)
IUPAC name 3,5-dichloro-N-(1,1-dimethylpropynyl)benzamide
Chemical Abstracts name 3,5-dichloro-N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propynyl)benzamide
CAS RN [23950-58-5] Development codes RH 315 (Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 256.1 M.f. C12H11Cl2NO Form Colourless, odourless powder. M.p. 155-156 ºC V.p. 0.058 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = c. 3.1-3.2 Henry 9.90 × 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 15 mg/l (25 ºC). In methanol, isopropanol 150, cyclohexanone, methyl ethyl ketone 200, dimethyl sulfoxide 330 (all in g/l). Moderately soluble in benzene, xylene, carbon tetrachloride. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether. Stability Decomposes above melting point. Degraded photolytically on soil thin films, DT50 13-57 d in artificial sunlight. In solution for 28 d (pH 5-9, 20 ºC) <10% loss.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibition. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots, with translocation. Uses Selective control of many annual and perennial grasses, and some broad-leaved weeds in fruit, vines, lettuce, endive, chicory, brassicas, oilseed rape, legumes, alfalfa, clover, trefoil, sainfoin, artichokes, sugar beet, roses, ornamental trees and shrubs, on fallow land, and in forestry. Also control of Poa annua in Bermuda grass, Zoysia, and certain other turf species. Used either pre-emergence or early post-emergence. Rates vary from 0.56-2.2 kg a.i./ha. Phytotoxicity Certain varieties of lettuce may be injured at higher dose rates. Formulation types GR; SC; WP. Compatibility Compatible with many other herbicides to extend weed spectrum.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (I. L. Adler et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1972, 55, 802; idem, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 443). Residues determined by glc of a derivative (idem, loc. cit.) or by glc with ECD. In drinking water, by gc with FID (AOAC Methods, 1995, 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews Pronamide: Reregistration Eligibility Decision, US EPA, May 1994. Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 8350, female rats 5620, dogs >10 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >3160 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to eyes and skin. Inhalation LC50 for rats >5.0 mg/l. NOEL Chronic studies indicate NOEL for dogs 300, rats 200, mice 13 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.08 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 8770, mallard ducks >14 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >4.7, carp >5.1 mg a.i./l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >5.6 mg a.i./l Bees Not hazardous to bees; LD50 >100 mg a.i./bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >346 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals For metabolism in animals and plants, see R. Y. Yih et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1971, 19, 314-324; J. D. Fisher, ibid., 1974, 22, 606-608; J. M. Cantier et al., Pestic. Sci., 1986, 17, 235. Plants See under Animals. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil (25 ºC) c. 30 d. For further metabolism in soil, see refs. given under Animals. Duration of residual activity in soil, following an application rate of 1-4 kg/ha, is c. 2-6 months. Koc 800. Kd ranges from 0.04 (0.01% o.m., pH 6.6) to 72.2 (16.9% o.m., pH 6.8) (H. J. Pedersen et al., Pestic. Sci., 1995, 44, 131).
|