Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; pyrimidinyloxybenzoic analogue
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pyrithiobac-sodium (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
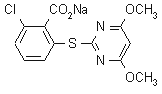
IUPAC name sodium 2-chloro-6-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylthio)benzoate
Chemical Abstracts name sodium 2-chloro-6-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylthio)benzoate
CAS RN [123343-16-8] sodium salt; [123342-93-8] parent acid Development codes KIH-2031 (Kumiai); DPX-PE 350 (Du Pont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >93%. Mol. wt. 348.7 M.f. C13H10ClN2NaO4S Form White solid. M.p. 233.8-234.2 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 4.80 × 10-6 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.6 (pH 5), -0.84 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.609 Solubility In water 264 (pH 5), 705 (pH 7), 690 (pH 9), 728 (unbuffered) (all in g/l, 20 °C). In acetone 812, methanol 270 × 103, n-hexane 10, dichloromethane 8.38 (all in mg/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable in water (32 d, pH 5-9, 27 °C) and to heat (15 d at 54 °C). pKa 2.34
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Selectivity is based on differing rates of metabolism. Uses Control of a wide range of broad-leaved weeds (morning glory, pigweed, cocklebur) and grasses pre- and post-emergence in cotton, at 70-105 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to cotton when applied as directed. Formulation types SP. Selected tradenames: 'Staple' (Du Pont, Kumiai)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3300, female rats 3200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.9 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 58.7, female rats 278 mg/kg b.w. daily; (78 w) for male mice 217, female mice 319 mg/kg b.w. daily. Other Non-mutagenic. Non-teratogenic (rats and rabbits). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >930, rainbow trout >1000, sheepshead minnow >145 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >1100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 107 mg/l; NOEC for S. capricornutum 22.8 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact) >25 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals More than 90% of radiolabelled pyrithiobac, applied orally and intravenously at 5 mg/kg to rats, was excreted in urine and faeces within 48 h; the major excreted metabolite was the O-desmethyl derivative. Pyrithiobac-sodium applied to hens and goats at 10 ppm diet was also substantially excreted, mostly unchanged, but the O-desmethyl derivative was a significant metabolite; residues in the kidney of both species were £0.06 ppm and were lower in liver, muscle and fat. Plants Amounts of pyrithiobac-sodium in cotton leaves rapidly decreased, following foliar application; at 62 dat, no residues were found; major metabolites found in foliage were the phenol formed by mono-demethylation, and its glucose conjugate. No residues were found in mature cotton seed on lint. Soil/Environment Microbial and photochemical degradation play a major role in degradation in the environment; DT50 in silty soil 60 d. Kd 0.32 (sandy loam), 0.60, 0.38, 0.75 (3 silty loam soils).
|