Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
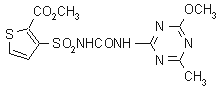
NOMENCLATURE
thifensulfuron-methyl
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 3-[[[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-2-thiophenecarboxylate
CAS RN [79277-27-3] Development codes DPX- M6316 (Du Pont)
thifensulfuron
Common name thifensulfuron (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO); thiameturon* (WSSA former name)
IUPAC name 3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)thiophen-2-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[[[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [79277-67-1]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Mol. wt. 387.4 M.f. C12H13N5O6S2 Form Colourless, odourless crystals. M.p. 176 ºC V.p. 1.7 × 10-5 mPa (25 ºC, Knudsen method) KOW logP = 0.20 (pH 5), 0.02 (pH 7) Henry 4.4 × 10-10 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.49. Solubility In water 230 (pH 5), 6270 (pH 7) (both in mg/l, 25 ºC). In hexane <0.1, xylene 0.2, ethanol 0.9, methanol, ethyl acetate 2.6, acetonitrile 7.3, acetone 11.9, dichloromethane 27.5 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable at 55 ºC. On hydrolysis, DT50 (45 ºC) 4.7 h (pH 3), 38 h (pH 5), 250 h (pH 7), 11 h (pH 9). pKa 4.0 (25 ºC)
thifensulfuron
Mol. wt. 373.4 M.f. C11H11N5O6S2
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicidal activity of thifensulfuron-methyl reported by R. M. Ambach et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1985, 39, 1220). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. Manufacturers Du Pont
APPLICATIONS
thifensulfuron-methyl
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Crop selectivity derives from metabolism (de-esterification) (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally and basipetally throughout the plant. Uses Used in winter and spring wheat, winter and spring barley, rye, triticale, oats, soya beans, pasture and maize (grain and fodder). Post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds and also loose silky-bent (Apera spica-venti) in winter and spring cereals. Application rates 9-60 g/ha. Normally used in combination with metsulfuron-methyl. Phytotoxicity Treated cereals may experience a temporary inhibition of growth and colour changes in the leaves, but these have no ultimate effect on the yield. Formulation types TB; WG.
ANALYSIS
For tech./formulations, by lc using u.v. For residues, by lc using column switching technique.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; mild but reversible irritant to eyes. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >7.9 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 100 mg/kg diet, for mice 7500 mg/kg diet, for dogs 1500 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for rats 25 mg/kg diet. NOEL in: reproduction (2-generation) in rats 2500 mg/kg diet; teratogenicity in rats 200 mg/kg daily, in rabbits >650 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.026 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames and three other mutagenicity tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV (TB, WG)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and Japanese quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LD50 (96 h) for rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish >100, catfish 360 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 970 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees. LD50 (topical) >12.5 mg/bee. Worms >2000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
thifensulfuron-methyl
Animals In mammals, following oral administration of thifensulfuron-methyl, 70-75% of the unchanged material is excreted in the urine and faeces. The primary degradation mechanism involves hydrolysis of the methoxycarbonyl group, O-demethylation of the heterocyclic ring, and hydrolysis of the sulfonylurea group. Plants In plants, complete degradation of thifensulfuron-methyl occurs within a few days. In tolerant crops such as cereals, the a.i. is almost completely hydrolysed within 24 h. DT50 in wheat c. 3-4 h, in soya beans c. 5-6 h. See also Mode of action. Soil/Environment Thifensulfuron-methyl is broken down in soil to non-active metabolites by microbial degradation and chemical hydrolysis. Under the same soil conditions, it decomposes 20-50 times more rapidly than metsulfuron-methyl. DT50 in soil c. 6-12 d under natural sunlight (c. 14 d in the absence of sunlight); DT50 (30 ºC, pH 8) only a few hours. Kd (silt loam) 0.6-8.6.
|