Insecticide
organophosphorus
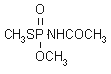
NOMENCLATURE
Common name acephate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, JMAF)
IUPAC name O,S-dimethyl acetylphosphoramidothioate
Chemical Abstracts name N-[methoxy(methylthio)phosphinoyl]acetamide
CAS RN [30560-19-1] EEC no. 250-241-2 Development codes Ortho 12 420 (Chevron) Official codes ENT 27 822
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is >97% pure. Mol. wt. 183.2 M.f. C4H10NO3PS Form Colourless crystals; (tech., a colourless solid). M.p. 88-90 ºC; (tech., 82-89 ºC) V.p. 0.226 mPa (24 ºC) KOW logP = -0.89 S.g./density 1.35 Solubility In water 790 g/l (20 ºC). In acetone 151, ethanol >100, ethyl acetate 35, benzene 16, hexane 0.1 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 50 d (pH 5-7, 21 °C), photodegradation DT50 (l = 253.7 nm) 55 h.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic insecticide. Uses Control of a wide range of chewing and sucking insects, e.g. aphids, thrips, lepidopterous larvae, sawflies, leaf miners, leafhoppers, cutworms, etc., at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha, in fruit (including citrus), vines, hops, olives, cotton, soya beans, peanuts, macadamia nuts, beet, brassicas, celery, beans, potatoes, rice, tobacco, ornamentals, forestry, and other crops. Of moderate persistence, with residual activity lasting c. 10-21 d. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to most crops, but marginal leaf burn may occur on Red Delicious apples. Formulation types AE; CG; GR; SP; WP.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (J. B. Leary, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 363). Residues determined by glc (idem, ibid.; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-H, 201-I; AOAC Methods, 1995, 985.22).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 59, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1447, female rats 1030 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >10 000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits); non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >15 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for dogs 0.75 mg/kg daily; LOEL for rats 0.25 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg [1990]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC hazard Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 350, chickens 852, ring-necked pheasants 140 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2050, rainbow trout >1000, channel catfish 2230, largemouth black bass 1725 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 67.2 mg/l; NOEC 43 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) >980 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for crayfish 750 ppm. Bees LD50 (contact) 1.2 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 22 974 mg/kg; NOEC 10 000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Metabolised to methamidophos (q.v.). Plants In plants, residual activity lasts for c. 10-15 d. The major metabolite is methamidophos (q.v.). Soil/Environment Readily biodegraded and non-persistent; soil DT50 2 d (aerobic) to 7 d (anaerobic). Aqueous DT50 (anaerobic metabolism) 6.6 d. Methamidophos (q.v.) has been identified as a soil metabolite. |