Insecticide, rodenticide
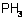
NOMENCLATURE
phosphine
IUPAC name phosphine
Chemical Abstracts name phosphine
Other names hydrogen phosphide CAS RN [7803-51-2] EEC no. 232-260-8
aluminium phosphide
Common name aluminium phosphide (E-ISO, accepted in lieu of a common name); aluminum phosphide (JMAF, accepted in lieu of a common name)
IUPAC name aluminium phosphide
Chemical Abstracts name aluminum phosphide
CAS RN [20859-73-8] EEC no. 244-088-0
magnesium phosphide
IUPAC name magnesium phosphide
Chemical Abstracts name magnesium phosphide
CAS RN [12057-74-8] EEC no. 235-023-7
zinc phosphide
Common name zinc phosphide (E-ISO, JMAF, accepted in lieu of a common name); phosphure de zinc (F-ISO, accepted in lieu of a common name)
IUPAC name trizinc diphosphide
Chemical Abstracts name zinc phosphide
CAS RN [1314-84-7] EEC no. 215-244-5
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
phosphine
Mol. wt. 34.0 M.f. H3P Form Colourless, odourless, flammable gas; (tech., garlic or rotting fish odour). M.p. -132.5 ºC B.p. -87.4 ºC V.p. High Henry 33 269 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density Gaseous 1.18 (air = 1) Solubility In water 26 cm3/100 ml (17 ºC). In ethanol 0.5, ether 2, oil of turpentine 3.25 (all in vol. phosphine per vol. solvent, 18 ºC). In cyclohexanol 285.6 cm3/100 ml (26 ºC). Stability Oxidised to phosphoric acid by oxidising agents and atmospheric oxygen. F.p. It is spontaneously flammable in air (due to the presence of traces of other hydrides of phosphorus) with an explosion limit of 26.1-27.1 mg/l
aluminium phosphide
Mol. wt. 58.0 M.f. AlP Form Dark grey or yellowish crystals. M.p. >1000 ºC V.p. Very low, even at 1000 ºC S.g./density 2.85 (25 °C) Stability Though stable when dry, it reacts with moist air, violently with acids, producing phosphine.
magnesium phosphide
Mol. wt. 134.9 M.f. Mg3P2 Form Yellow-green crystals. M.p. >750 °C S.g./density 2.055 Stability Stable when dry, but reacts with atmospheric moisture, and violently with acids, producing phosphine; used to generate this fumigant, reacting more rapidly than aluminium phosphide.
zinc phosphide
Composition Tech. grade is 80-95% pure. Mol. wt. 258.1 M.f. P2Zn3 Form Amorphous grey-black powder, with a garlic-like odour. M.p. 420 ºC (when heated in the absence of oxygen) V.p. Negligible in the dry state S.g./density 4.55 Solubility Practically insoluble in water (decomposes slowly). Slightly soluble in carbon disulfide and benzene. Practically insoluble in alcohols. Stability Stable when dry, but decomposes slowly in moist air; it is decomposed violently by acids to produce phosphine, which is a potent mammalian poison, and impurities which render the gas spontaneously flammable.
COMMERCIALISATION
phosphine
Manufacturers United Phosphorus
aluminium phosphide
History Introduced as a source of fumigant insecticide by Dr. Werner Freyberg Chemische Fabrik (now Detia Freyberg). Patents GB 461997; US 2117158 Manufacturers Ag Pesticides; Aimco; Detia Freyberg; Excel; Shenzhen Jiangshan; United Phosphorus; Young IL
magnesium phosphide
History Introduced by Degesch AG to generate phosphine and so fumigate stored foodstuffs. Patents DE 923999 to Edmund Manufacturers Detia Freyberg; United Phosphorus
zinc phosphide
History It has long been used as a poison against rodents. Manufacturers Ag Pesticides; Aimco; Excel; Hacco; Liphatech; Motomco; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
aluminium phosphide
Mode of action Insecticide and rodenticide which is a respiratory, metabolic, and nerve poison. Evolves a non-flammable mixture of phosphine (the toxicant), ammonia and carbon dioxide. Uses Fumigation control of insect and rodent pests in stored grains (wheat, rye, barley, rice, sorghum, maize, etc.), seed grains, grain products (flour, noodles, semolina, etc.), pulses (peas, beans, lentils, etc.), tobacco, tapioca (roots and flour), oil seeds, expeller cake, nuts, nut kernels, dried fruit, coffee beans, cocoa beans, tea, etc.; and in empty warehouses, silos, packing materials, transport containers, etc. Phytotoxicity Living plants, fresh vegetables and fruits, with few exceptions, should not be fumigated. Formulation types GE; Fumigant. Selected tradenames: 'Agtoxin' (Ag Pesticides); 'Al-Phos' (Aimco); 'Celphide' (Excel); 'Celphos' (Excel); 'Phostek' (Killgerm); 'Phostoxin' (Detia Degesch); 'Quickphos' (United Phosphorus); 'Shaphos' (Sanonda)
magnesium phosphide
Mode of action Insecticide and rodenticide which is a respiratory, metabolic, and nerve poison. Liberates phosphine, which is the toxicant. Uses As for aluminium phosphide. Also used for control of moles, voles, rats, hamsters, and rabbits by fumigation of burrows. Phytotoxicity Living plants, fresh vegetables and fruits, with few exceptions, should not be fumigated. Formulation types GE; Fumigant. Selected tradenames: 'Magnaphos' (United Phosphorus); 'Magtoxin' (Detia Degesch)
zinc phosphide
Mode of action Rodenticide (for single ingestion). Reacts with stomach acids to liberate poisonous phosphine, which enters the bloodstream, and results in damage to the liver, kidneys and heart. Uses Bait rodenticide for control of rats, mice, voles, ground squirrels, and gophers. Also used in tracking powder form for house mouse control. Formulation types AB; CP; PA; RB; SB. Selected tradenames: 'Agzinphos' (Ag Pesticides); 'Commando' (Excel); 'Ratol' (United Phosphorus); 'Rattekal-Plus' (Frunol); 'Zawa' (Sanonda); 'Zinc-Tox' (Aimco)
OTHER TRADENAMES
aluminium phosphide
'Celphine' (Excel); 'Detia-Gas-Ex-B' (and Ex-T, Ex-P) (Detia Degesch); 'Fumitoxin' (Pestcon); 'Gran Quick Phos' (Agricultura Nacional); 'L-Fume' (Excel); 'Luxan Talunex' (Luxan); 'Talunex' (Luxan) Discontinued names: 'Amos Talunex' * (Luxan); 'DeliciaGastoxin' * (Delicia)
magnesium phosphide
'Degesch Plates' (Detia Degesch); 'Fumi-Cel' (Degesch America); 'Fumi-Strip' (Degesch America) Discontinued names: 'Detiaphos' * (Detia Degesch)
zinc phosphide
'Arrex' (BASF); 'Foke BA' (Vipesco); 'Ridall-Zinc' (Liphatech) Discontinued names: 'Denkarin Grains' * (Denka)
ANALYSIS
phosphine
Phosphine present during fumigation can be determined using commercially available detector tubes, by glc (B. Chakrabarti & H. E. Wainman, Chem. Ind. (London), 1972, p. 300) or by aspiration through aqueous mercuric chloride and measuring the change in electrical conductivity (A. H. Harris, Proc. GASGA Tech. Seminar, TDRI, Slough, 1986). Methods for residues in foods reviewed, with details by J. L. Daft in Comp. Anal. Profiles, p. 274.
aluminium phosphide
Product and residue analysis depend upon determining the phosphine liberated by acid treatment. Measurement is by glc (B. Berck et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1970, 18, 143; T. Dumas, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1978, 61, 51; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part II, M8; K. A. Scudamore, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 251; K. A. Scudamore & G. Goodship, Pestic. Sci., 1986, 37, 385).
magnesium phosphide
Product analysis by determining the phosphine liberated on treatment with acid, by glc (T. Dumas, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1978, 61, 51) or phosphate produced after reaction with bromine water (R. B. Bruce et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1962, 10, 18).
zinc phosphide
Product analysis by reaction with acid, the phosphine produced is estimated by titration (CIPAC Handbook, 1970, 1, 703), or oxidised to phosphoric acid which is estimated by standard methods (J. W. Elmore & F. R. Roth, J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem., 1943, 26, 559; 1947, 30, 213; B. L. Griswold et al., Anal. Chem., 1951, 23, 192).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
phosphine
Reviews FAO/WHO 6, 7 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Skin and eye No absorption through the skin. Inhalation Powerful respiratory poison. LC50 (4 h) for rats 11 ppm (0.015 mg/l) (R. S. Waritz & R. M. Brown, Am. Ind. Assoc. J., 36, 452-458 (1975)). Inhalation at 10 mg/m3 can cause death within 6 h, and at 300 ml gas/m3 for one hour, there is danger to life. No symptoms of chronic poisoning are observed. ADI (JMPR) Not necessary on basis of no residue in food [1966]. Other Phosphine is a potent, acute mammalian poison, but feeding trials with fumigated foodstuffs have shown no chronic effects on rats (U. Hackenberg, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 1972, 23, 147). Toxicity class EPA (formulation) I
aluminium phosphide
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 8.7 mg/kg. EC hazard F; R15/29| T+; R28| R32
magnesium phosphide
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 11.2 mg/kg. EC hazard F; R15/29| T+; R28
zinc phosphide
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 45.7, sheep 60-70 mg/kg (M. A. Nekrasova, Sb. Rab., Leningr. Vet. Inst., 1964, No. 25, 372). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 2000-5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC hazard F; R15/29| T+; R28| R32
ECOTOXICOLOGY
phosphine
Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 9.7 ´ 10-3 ppm. Daphnia EC50 (24 h) 0.2 mg/l.
zinc phosphide
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 37.5, bobwhite quail 13.5, pheasants 9 mg/kg (D. W. Hayne, Mich. Agric. Exp. Stn., Q. Bull., 1951, No. 33, 412); for fowls, the lethal dose is 7-17 mg/kg (G. D. Shearer, J. Comp. Pathol. Therap., 1945, 55, 301). Fish Acute LC50 for bluegill sunfish 0.8, rainbow trout 0.5 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 73 (WHO, 1988; a review of phosphine and metal phosphides). Animals In mammals, phosphine is probably metabolised to non-toxic phosphates. Plants In stored products, phosphine undergoes oxidation to phosphoric acid. |