Insecticide, plant growth regulator
carbamate
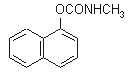
NOMENCLATURE
Common name carbaryl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, BAN); NAC (JMAF); sevin* (former exception, USSR)
IUPAC name 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 1-naphthalenyl methylcarbamate
CAS RN [63-25-2] EEC no. 200-555-0 Development codes UC 7744 (Union Carbide) Official codes OMS 29; OMS 629; ENT 23 969
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is ≥99% pure. Mol. wt. 201.2 M.f. C12H11NO2 Form Colourless to light tan crystals. M.p. 142 ºC V.p. 4.1 × 10-2 mPa (23.5 ºC) KOW logP = 1.85 Henry 7.39 × 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.232 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 120 mg/l (20 ºC). Readily soluble in polar organic solvents. In dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide 400-450, acetone 200-300, cyclohexanone 200-250, isopropanol 100, xylene 100 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable under neutral and weakly acidic conditions. Hydrolysed in alkaline media to 1-naphthol; DT50 c. 12 d (pH 7), 3.2 h (pH 9). Stable to light and heat. F.p. 193 °C
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Weak cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action, and slight systemic properties. Uses Control of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, and other chewing and sucking insects, at 0.25-2.0 kg a.i./ha, on more than 120 different crops, including vegetables, tree fruit (including citrus), mangoes, bananas, strawberries, nuts, vines, olives, okra, cucurbits, peanuts, soya beans, cotton, rice, tobacco, cereals, beet, maize, sorghum, alfalfa, potatoes, ornamentals, forestry, etc. Control of earthworms in turf. Used as a growth regulator for fruit thinning of apples. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic if used as directed. Under certain conditions, some varieties of apple and pear may be injured. Formulation types DP; GR; OF; RB; SC; TK; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials such as Bordeaux mixture, lime, and lime sulfur.
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectroscopy (AOAC Methods, 1995, 976.04; CIPAC Handbook, 1970, 1, 185; 1980, 1A, 1113; FAO Specification (CP/55)) or by hplc (G. W. Sheehan, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 157). Residues determined by glc (ibid., 1972, 6, 478; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M13; AOAC Methods, 1995, 975.40; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733), by hplc (AOAC Methods, 1995, 985.23), by colorimetry (ibid., 964.18) or by tlc (ibid., 968.26). For methods in drinking water, see AOAC Methods, 1995, 991.06.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 89 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 12 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 264, female rats 500, rabbits 710 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >4000, rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant, mild skin irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 3.28 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 200 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.003 mg/kg b.w. [2000]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) I ('Tercyl' 85WP), II ('Sevin' 80S), III EC hazard R40| Xn; R22| N; R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for young mallard ducks >2179, young pheasants >2000, Japanese quail 2230, pigeons 1000-3000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.3, sheepshead minnow 2.2, bluegill sunfish 10 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.006 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.1 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 0.0057 mg/l; LC50 (48 h) for Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 2.7 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees; LD50 (topical) 1 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (28 d ) 106-176 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Toxic to beneficial insects.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 153 (WHO, 1994); 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In mammals, carbaryl does not accumulate in body tissues, but is rapidly metabolised to non-toxic substances, particularly 1-naphthol. This, together with the glucuronic acid conjugate, is eliminated predominantly in the urine and faeces. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants Metabolites are 4-hydroxycarbaryl, 5-hydroxycarbaryl and methylol-carbaryl. Soil/Environment Under aerobic conditions, carbaryl at 1 ppm degraded with DT50 7-14 d in a sandy loam and 14-28 d in a clay loam.
|