Insecticide
carbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name carbosulfan (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
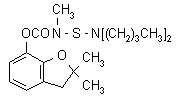
IUPAC name 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran-7-yl (dibutylaminothio)methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl [(dibutylamino)thio]methylcarbamate
CAS RN [55285-14-8] EEC no. 259-565-9 Development codes FMC 35 001 Official codes OMS 3022
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 380.5 M.f. C20H32N2O3S Form Orange to brown clear, viscous liquid. B.p. 124-128 ºC V.p. 0.041 mPa (25 ºC) Henry 5.20 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.056 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.3 ppm (25 ºC). Miscible with most organic solvents, e.g. xylene, hexane, chloroform, dichloromethane, methanol, ethanol, acetone, etc. Stability Hydrolysed in aqueous media; DT50 (25 ºC) in pure water <1 h (pH 4), 22 h (pH 6), 7.6 d (pH 7), 14.2 d (pH 8), >58.3 d (pH 9). F.p. 95 ºC (closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by E. C. Maitlen & N. A. Sladen (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf., 1979, 2, 557). Introduced by FMC Corp. Manufacturers FMC; Kuo Ching; Zhejiang
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor; activity is due to in vivo cleavage of the N-S bond, resulting in conversion to carbofuran. Mode of action Systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of soil-dwelling and foliar insect pests. Examples of uses include control of millipedes, springtails, symphylids, wireworms, pygmy mangold beetles, frit flies, white grubs, aphids, caterpillars, flea beetles, Colorado beetles, stem borers, leafhoppers, planthoppers, codling moth, scales and free-living nematodes. The product is used in a wide range of crops, e.g. cotton, sugar beet, potatoes, rice, top fruit, citrus, maize, vegetables, sugar cane and coffee. Formulation types CS; DP; EC; GR; UL; WP. Compatibility Compatible with liquid fertilisers. Selected tradenames: 'Marshal' (FMC); 'Posse' (FMC); 'Spi' (FMC); 'Suden' (Sanonda)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Advantage' (FMC); 'Beam' (FMC); 'Gazette' (FMC); 'Agrostar' (AgroSan); 'Pilarsufan' (Pilarquim); 'Weilin' (Zhejiang) mixtures: 'Gazette Prince' (+ fipronil) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rp hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 35). Residues determined by glc (B. Leppert et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1983, 31, 220; 1984, 32, 1441) or by hplc. Details available from FMC Agricultural Chemicals Group.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 47, 49 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 250, female rats 185 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant; moderate skin irritant. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for male rats 1.53, female rats 0.61 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) (oncogenic) for rats and mice 20 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1986]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) I (4 EC), II (2.5 EC) EC hazard T; R23/24| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 8.1, quail 82, pheasants 20 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.015, trout 0.045 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.5 mg/l. Algae (96 h) 20 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In rats, following oral administration, rapidly metabolised by hydrolysis, oxidation and conjugation, forming carbofuran methylol, carbofuran phenol, and their 3-hydroxy and 3-keto derivatives; the metabolites are rapidly excreted. Plants Metabolites include carbofuran (q.v.) and 3-hydroxycarbofuran. Soil/Environment In soil, rapidly degraded under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions; DT50 c. 2-5 d; DT90 <3-38 d; the principal metabolite is carbofuran (q.v.). Under field conditions, carbosulfan and carbofuran are unlikely to leach to groundwater. |