Insecticide, acaricide
pyrazole (acaricide) analogue
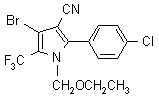
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chlorfenapyr (BSI, pa ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethylpyrrole-3-carbonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
CAS RN [122453-73-0] Development codes AC 303,630; CL 303,630 (both Cyanamid); MK-242 (Mitsubishi)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 407.6 M.f. C15H11BrClF3N2O Form White solid. M.p. 100-101 ºC KOW logP = 4.83 Solubility Practically insoluble in water. Soluble in acetone, diethyl ether, dimethyl sulfoxide, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile, and alcohols.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Under development by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG).
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Oxidative removal in vivo of the N-ethoxymethyl group generates the active species, which is a mitochondrial uncoupler. Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with mainly stomach and some contact action. Exhibits good translaminar but limited systemic activity in plants. Uses Control of many species of insects and mites, including those resistant to carbamate, organophosphate and pyrethroid insecticides and also chitin-synthesis inhibitors, in cotton, vegetables, citrus, top fruit, vines and soya beans. Among pests resistant to conventional products which are controlled by chlorfenapyr are Brevipalpus phoenicis (leprosis mite), Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Colorado potato beetle), Helicoverpa spp., Heliothis spp., Plutella xylostella (diamond-back moth) and Tetranychus spp. Its use in resistance management programmes for control of various cotton pests is under evaluation. Phytotoxicity No phytotoxicity observed at field use rates. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected tradenames: 'Pirate' (cotton) (BASF); 'Stalker' (BASF)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Alert' (citrus, cotton) (BASF); 'Chu-Jin' (China) (BASF); 'Grizli' (E. Europe) (BASF); 'Intrepid' (Europe) (BASF); 'Rampage' (S.E. Asia) (BASF); 'Secure' (ornamentals) (BASF); 'Kotetsu' (Japan) (BASF, Mitsubishi Chemical)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues by hplc. Details from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 441, female rats 1152 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 for rats 1.9 mg tech./l air. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames, CHO/HGPRT, mouse micronucleus and unscheduled DNA synthesis tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 10, bobwhite quail 34 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 9.4, bobwhite quail 132 ppm. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 500 mg/l. LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 7.44, bluegill sunfish 11.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) 6.11 mg/l. Bees LD50 0.2 mg/bee. |