Insecticide
NOMENCLATURE
emamectin benzoate
CAS RN [155569-91-8]; formerly [137512-74-4] and [179607-18-2] Development codes MK 244 (Merck)
emamectin
Common name emamectin (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI); emamectine ((f) pa F-ISO)
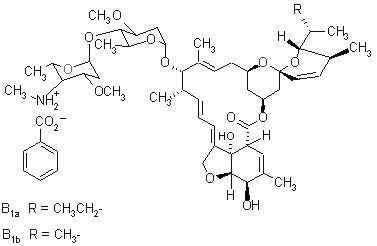
IUPAC name A mixture containing 90% of (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S,13S,20R,21R,24S)-6'-[(S)-sec-butyl]-21,24-dihydroxy-5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-2-oxo-3,7,19-trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene-6-spiro-2'-(5',6'-dihydro-2'H-pyran)-12-yl 2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-4-O-(2,4,6-trideoxy-3-O-methyl-4-methylamino-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-a-L-arabino-hexopyranoside and 10% of (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S,13S,20R,21R,24S)-21,24-dihydroxy-6'-isopropyl-5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-2-oxo-3,7,19-trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene-6-spiro-2'-(5',6'-dihydro-2'H-pyran)-12-yl 2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-4-O-(2,4,6-trideoxy-3-O-methyl-4-methylamino-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-a-L-arabino-hexopyranoside
Chemical Abstracts name (4"R)-5-O-demethyl-4"-deoxy-4"-(methylamino)avermectin A1a + (4"R)-5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-4"-deoxy-4"-(methylamino)-25-(1-methylethyl)avermectin A1a (9:1)
CAS RN [119791-41-2]; formerly [123997-28-4] and [137335-79-6]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
emamectin benzoate
Composition A mixture of emamectin B1a (≥90%) and emamectin B1b (≤10%), as their benzoate salts. Mol. wt. 1008.3 (B1a); 994.2 (B1b) M.f. C56H81NO15 (B1a); C55H79NO15 (B1b) Form White to off-white powder. M.p. 141-146 °C V.p. 4 × 10-3 mPa (21 °C) KOW logP = 5.0 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.20 (23 °C) Solubility In water 0.024 g/l (pH 7, 25°C).
emamectin
Mol. wt. 886.1 (B1a); 872.1 (B1b) M.f. C49H75NO13 (B1a); C48H73NO13 (B1b)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovery and initial development was by Merck & Co., Inc. (now Syngenta AG). First sales in Israel and Japan in 1997. Manufacturers Merck & Co.
APPLICATIONS
emamectin benzoate
Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide which penetrates leaf tissues by translaminar movement. Uses For control of Lepidoptera on vegetables, brassicas and cotton, at up to 16 g/ha, and in pine trees, at 5-25 g/ha. Formulation types EC; SG.
ANALYSIS
Product and residues determined by hplc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
emamectin benzoate
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 76-89 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. It is not irritant to skin, and has no sensitising potential. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 2.12-4.44 mg/m3. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 0.25 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.0025 mg/kg. Other Not tumorigenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
emamectin benzoate
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 46, bobwhite quail 264 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 570, bobwhite quail 1318 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 174, sheepshead minnow 1430 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 0.99 mg/l. Algae >94 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Worms >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Emamectin benzoate is partially metabolised but rapidly cleared (DT50 following oral dosing 34-51 h), indicating that it has no potential for bioaccumulation. Plants Metabolism has been investigated in lettuce, cabbage and sweet corn. It is non-systemic, and rapidly degrades in sunlight to various complex residues in which undegraded parent is the only significant residue. The residues were very low. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded
|