Insecticide
organophosphorus
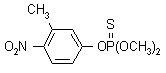
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenitrothion (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA, BAN); MEP (JMAF)
IUPAC name O,O-dimethyl O-4-nitro-m-tolyl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-dimethyl O-(3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate
CAS RN [122-14-5] EEC no. 204-524-2 Development codes Bayer 41831; S-5660; S-1102A (all to Bayer); AC 47 300 (Cyanamid) Official codes OMS 43; OMS 223; ENT 25 715
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 277.2 M.f. C9H12NO5PS Form Yellow-brown liquid, with a faint characteristic odour. M.p. 0.3 °C B.p. 140-145 ºC/0.1 mmHg (decomp.) V.p. 18 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.43 (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.328 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 14 mg/l (30 ºC). Readily soluble in alcohols, esters, ketones, aromatic hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons. In hexane 24, isopropanol 138 (both in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Relatively stable to hydrolysis under normal conditions: DT50 (est.) 108.8 d (pH 4), 84.3 d (pH 7), 75 d (pH 9) (22 ºC). F.p. 157 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by Y. Nishizawa et al. (Bull. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1960, 24, 744; Agric. Biol. Chem., 1961, 25, 605). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and, independently, by Bayer AG and later by American Cyanamid Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents BE 594669 to Sumitomo; BE 596091 to Bayer Manufacturers Rallis; Shenzhen Jiangshan; Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of chewing, sucking, and boring insects in cereals, soft fruit, tropical fruit, vines, rice, sugar cane, vegetables, turf, and forestry. Also used as a public health insecticide for control of household insects (flies, cockroaches, and other insects) by application to breeding sites; for control of flies in animal houses; for control of stored product insect pests; for control of mosquito larvae (as a vector control agent for malaria); and for control of locusts. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended. Cotton, brassicas, and some fruits may be injured by high rates of application. Russetting is possible with some apple varieties. Formulation types AE; DP; EC; GR; UL; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline compounds. Selected tradenames: 'Folithion' (Bayer); 'Sumithion' (Sumitomo); 'Cekutrotion' (Cequisa); 'Dicofen' (PBI); 'Farmathion' (Sanonda); 'Fentron' (Efthymiadis); 'Shaminliulin' (Shenzhen Jiangshan)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Accothion' (BASF); 'Chemition' (Chemia); 'Cyfen' (BASF); 'Durakil' (Antec); 'EC-Kill' (Antec); 'Fenithion' (Agrochem); 'Novathion' (Cheminova); 'Owadofos' (Azot); 'Pilarthion' (Pilarquim); 'Senthion' (Vapco); 'Visumit' (Vipesco) mixtures: 'Broxer' (+ esfenvalerate) (Sumitomo); 'Fency' (+ cypermethrin) (Efthymiadis); 'Fenikill' (+ fenvalerate) (Vapco); 'Kasu-rab-sumibassa' (+ fenobucarb+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate+ phthalide) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rab-valida-sumi' (+ kasugamycin+ validamycin) (Hokko); 'Turbair Grain Store Insecticide' (+ permethrin+ resmethrin) (Graincare); 'Vifensu' (+ fenvalerate) (Vipesco) Discontinued names: 'Micromite' * (Grampian) mixtures: 'Anthiomix' * (+ formothion) (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2117; AOAC Methods, 1995, 989.02) or by the Averell & Norris method (CIPAC Handbook, 1980, 1A, 1255; FAO Specification (CP/62)). Residues determined by glc (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-H, 201-I; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5; Analyst (London), 1980, 105, 515; 1985, 110, 765). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 89, 91 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats c. 1700, female rats 1720 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats c. 810, female rats 840 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2210 mg/m3 (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 10 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 50 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.005 mg/kg b.w. [2000]. Other Not carcinogenic, mutagenic, embryotoxic or teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC hazard Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail 23.6, mallard ducks 1190 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 4.1 mg/l. LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2.5, rainbow trout 1.3 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.0086 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.3 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Other beneficial spp. Highly toxic to non-target arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 133 (WHO, 1992), 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Fenitrothion is rapidly excreted in the urine and faeces. After 3 d, c. 90% has been excreted by rats, mice and rabbits. The most important metabolites are dimethylfenitrooxon and 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol. Plants Fenitrothion applied in the forest (balsam fir and spruce foliage) degraded, with DT50 4 d; 70-85% is degraded within 2 weeks. Similar results are obtained in conifer foliage and cocoa trees. Major metabolites are 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol, the oxygen analogue and their decomposition products desmethylfenitrothion, dimethylphosphorothionic acid and phosphorothionic acid. Soil/Environment DT50 12-28 d under upland conditions, 4-20 d under submerged conditions. The major metabolites under upland conditions are 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol and CO2, whereas, under submerged conditions, the major decomposition product is aminofenitrothion. |