Acaricide, insecticide
pyrethroid
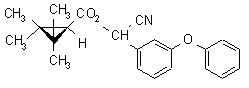
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenpropathrin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI); fenpropathrine ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl 2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [64257-84-7] racemate; [39515-41-8] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 254-485-0 Development codes S-3206 (Sumitomo) Official codes OMS 1999
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 349.4 M.f. C22H23NO3 Form Yellow-brown solid (tech.). M.p. 45-50 ºC V.p. 0.730 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 6 (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.15 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 14.1 mg/l (25 ºC). In xylene, cyclohexanone 1000, methanol 337 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Decomposed in alkaline solutions. Exposure to light and air leads to oxidation and loss of activity.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by Y. Fujita (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1981, No. 38, p. 21). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and, in some countries, by Shell International Chemical Co. (now BASF AG). Patents GB 1356087; US 3835176 Manufacturers Agrochem; BASF; Shenzhen Jiangshan; Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Acaricide and insecticide with repellent, and contact and stomach action. Uses Control of many species of mites (except rust mites) and insects (e.g. whitefly, lepidopterous larvae, leaf miners, leafworms, bollworms, etc.) on pome fruit, citrus fruit, vines, hops, vegetables, ornamentals (including ornamental trees), cotton, field crops, and glasshouse crops (cucurbits, tomatoes, ornamentals, etc.). Formulation types EC; SC; UL; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected tradenames: 'Danitol' (Valent, Sumitomo); 'Herald' (BASF); 'Meothrin' (Sumitomo); 'Rody' (Sumitomo, BASF); 'Digital' (Sanonda)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Fenthrin' (Agrochem); 'Jiaqingjuzhi' (Shenzhen Jiangshan); 'Vimite' (Vipesco) mixtures: 'Virk' (+ etoxazole) (Yashima, Sumitomo)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By hplc (S. Sakaue et al., Agric. Biol. Chem., 1982, 46, 2165) or by glc with FID (idem, ibid.; Y. Takimoto et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 69). Residues determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.); details available from Sumitomo Chemical Co.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). See also A. J. Gray & D. M. Soderlund, Chapt. 5 in "Insecticides". Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 70.6, female rats 66.7 mg/kg (in corn oil). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 1000, female rats 870, rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; mild eye irritant (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >96 mg/m3. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1993]. Other Non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC hazard T+; R26| T; R25| Xn; R21| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 1089 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.95 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Degraded principally by photolysis, DT50 2.7 w in river water. Duration of activity in soil c. 1-5 d. Metabolites are listed in Pestic. Sci., 1985, 16, 119. |