Insecticide, nematicide
organophosphorus
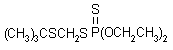
NOMENCLATURE
Common name terbufos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA)
IUPAC name S-tert-butylthiomethyl O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name S-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)thio]methyl] O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [13071-79-9] EEC no. 235-963-8 Development codes AC 92 100 (Cyanamid) Official codes ENT 27 920
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is ³85% pure. Mol. wt. 288.4 M.f. C9H21O2PS3 Form Slightly yellow liquid, with a mercaptan-like odour. M.p. -29.2 ºC B.p. 69 ºC/0.01 mmHg V.p. 34.6 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.77 S.g./density 1.105 (24 ºC) Solubility In water 4.5 mg/l (27 ºC). Readily soluble in most organic solvents, e.g. aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, alcohols, acetone c. 300 g/l. Stability Stable for more than 2 years at room temperature. Decomposes on prolonged heating above 120 ºC. Hydrolysis DT50 for tech. 2-3 d (pH 4-9). F.p. 88 ºC (Tag open cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by E. B. Fagan (Proc. Br. Insectic. Fungic. Conf. 7th, 1973, 2, 695). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG) and first marketed in 1974. Manufacturers BASF; Rotam; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Soil insecticide and nematicide with stomach and contact action. Uses Has effective initial and residual activity against soil-dwelling arthropods. Soil application of granules controls Diabrotica spp. larvae in maize, Tetanops myopaeformis in sugar beet, Delia spp. larvae in cabbages and onions, Diplopoda, Symphyla, Elateridae, and other soil-dwelling arthropods. Various above-ground pests are also controlled on plants grown in terbufos-treated soil. It has nematicidal activity, controlling Radopholus similis, Meloidogyne incognita and Helicotylenchus spp. in bananas, and Ditylenchus dipsaci in sugar beet. Rates 0.25-2.0 kg a.i./ha. Formulation types GR. Selected tradenames: 'Contraven' (BASF); 'Counter' (BASF, Dow AgroSciences); 'Cyanater' (Caffaro); 'Hunter' (United Phosphorus); 'Pilarfox' (Pilarquim); 'Terborox' (Rotam); 'Terfos' (Efthymiadis); 'Tertin' (Sanonda)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Plydax' (BASF); 'Aragran' (Dr Maag)
ANALYSIS
Formulations and residues determined by glc (E. J. Orloski, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 11, 165). In drinking water, by gc with FID (AOAC Methods, 1995, 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 56, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male albino rats 1.6 mg tech./kg; for female albino mice 5.4 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 9.8, rabbits 1.0 mg/kg. Skin and eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 0.0061 mg a.i./l air, for females 0.0012 mg/l air. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 1 mg/kg diet showed no adverse effects other than cholinesterase depression and associated syndrome. ADI (JMPR) 0.0002 mg/kg b.w. [1989]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC hazard T+; R27/28
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 185, ring-necked pheasants 145 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.01, bluegill sunfish 0.004 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees when used as directed. LD50 for honeybees by topical application 4.1 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Degradation in animals is the same as in soil. Plants Degradation in plants is the same as in soil. Soil/Environment Oxidative and hydrolytic degradation occurs in soil. No accumulation. Half-life in soil is 9-27 d.
|