Plant growth regulator
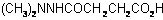
NOMENCLATURE
Common name daminozide (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name N-dimethylaminosuccinamic acid
Chemical Abstracts name butanedioic acid mono(2,2-dimethylhydrazide)
Other names SADH CAS RN [1596-84-5] EEC no. 216-485-9 Development codes B-995
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade daminozide is >99% pure. Mol. wt. 160.2 M.f. C6H12N2O3 Form Tech. is a white powder, with a faint amine-like odour. M.p. 157-164 ºC V.p. 22.7 mPa (23 ºC) KOW logP = -1.50 (pH 5, 7 and 9, 21 ºC) Solubility In distilled water 100 g/kg (25 ºC). In methanol 50, acetone 25 (both in g/kg, 25 ºC). Insoluble in hydrocarbons. Stability No measurable hydrolysis over 30 d at pH 5, 7 and 9. Hydrolysed by acids and alkalis on heating. Solutions are slowly decomposed by light. pKa 4.68 (20 ºC)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Plant growth regulator reported by J. A. Riddell et al. (Science, 1962, 136, 391). Introduced by Uniroyal Chemical Co., Inc. (now part of CK Witco Corp.). Patents US 3240799; US 3334991 Manufacturers Fine; Uniroyal
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Interferes with gibberellic acid biosynthesis. Mode of action Absorbed by the leaves, with translocation throughout the plant. Uses To produce more compact plants (by inhibition of internodal elongation) of chrysanthemums, azaleas, hydrangeas, poinsettias, and other ornamentals. Formulation types SP. Compatibility Incompatible with wetting agents, alkaline materials, oils, and copper-containing compounds. Selected tradenames: 'Alar' (Uniroyal); 'B-Nine' (Uniroyal)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Dazide' (Fine) Discontinued names: 'Kylar' * (Uniroyal)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Details available from Uniroyal. Residues determined by glc of a derivative (J. R. Lane, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1967, 5, 499) or by alkaline hydrolysis to liberate 1,1-dimethylhydrazine which is determined colorimetrically (Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 697; V. P. Lynch, ibid., 1976, 8, 491).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 62, 64 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.1 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 188 mg/kg b.w. daily, for rats 5 mg/kg b.w. daily. Non-oncogenic in 2 y feeding trials in rats and mice at 10 000 mg/kg diet. NOEL for teratogenicity and embryotoxicity in rabbits was 300 mg/kg diet. In 3-generation reproductive study, NOAEL for rats was 50 mg/kg b.w. daily. Non-mutagenic in in vivo test. ADI (JMPR) 0.5 mg/kg b.w., for daminozide containing <30 mg 1,1-dimethylhydrazine/kg [1991]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV EC hazard R40
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >10 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 149, bluegill sunfish 423 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) 76 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Chlorella 180 ppm. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 >100 mg/bee (85% formulation). Worms LC50 for earthworms >632 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Plants Metabolites include 1,1-dimethylhydrazine. Soil/Environment Daminozide quickly dissipates in soil with most residues becoming bound, with some CO2 formation. In aerobic soil, half of the daminozide is no longer recoverable after 17 h. No 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) or N-nitrosodimethylamine were detected. In soil under anaerobic conditions, half of the daminozide had dissipated in 7.5 days. The major products were bound residues and CO2. In a field study on bare ground, about 90% of the daminozide had disappeared after 7 days. Neither hydrolysis nor photolysis are significant pathways for the degradation of daminozide. |