|
The Outlook of Chinese Talc Trade
by Dr Jia Xiu Zhuang* Prof Jiang De Yu**
Abstract: China is the largest talc exporter although its quantity dropped
dramatically in recent years. The export prices have been increasing since
1996 when the quota was charged, and a further increase by USD5-15/mt
is expected within the next three to five years. China dominates on the
supply of white talc in the world. Asia is the largest market for Chinese
talc, while North America and West Europe are the fastest growing regions.
With the decline of talc in paper filler market, Chinese low grade talc
will combat for serious sales opportunities. On the other hand, the supply
of upper grade lump talc will fall short of the demand as the results
of two contrary trends of increasing requirement for talc filler PP in
automobile industry and the decreasing output of Chinese white talc. The
growth rate of talc import by China is remarkable since 1990. But it is
unrealistically optimistic to think that Chinese talc will enter a bright
era.
EXPORT
1. Review
China is the largest talc producer as well as the largest exporter in
the world. The export is the principal driving force for the development
of Chinese talc industry.
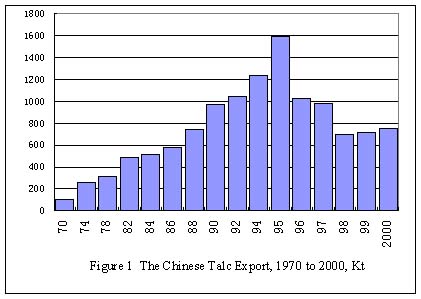
Figure 1 illustrates Chinese talc export between 1970 and 2000. In the
period of 1970 to 1995, Chinese talc export enjoyed a rapid growth of
annual rate 5.95%. The export quantity in 1970 was only 104.9 Kt, it reached
an all time high of 1.59 million tons, amounting to USD83.15 millions
in 1995, which accounted for the 67% of talc quantity traded worldwide
in the same year. China has had the leading shares on the world talc trade
since 1980s.
However, the export dropped dramatically since 1996.It was only 696.5
Kt in 1998, and 751.2 Kt in 2000,which was similar to the export in 1988.The
main reasons causing the dropping are as follows:
- Since 1996, the export quota was charged and the quantity was limited
by the government, which were 1000 Kt in 1996 and 1997,and down to 700
Kt after 1998. Despite Chinese talc export was subject to the quota
long time ago, the quota was not charged and the quantity was not limited
strictly until 1996. In order to save the quota charges, a large quantity
of talc, which should be shipped in 1996, was shifted to 1995 to export.
This made the export in 1995 larger than usual.
- The major market of Chinese talc is in Asia. The 65-95% of the export
talc is destined to Asian countries. The requirement of Asian market
had a crucial effect on Chinese talc export. Asian financial crisis
occurred in 1997 was seriously detrimental on the economies of some
Asian countries, resulting in the decline of talc import from China(Refer
to Table 1).
Table 1 Talc Import from China by Countries, 1995 to 2000, Kt
| Year |
Japan |
Korea |
Thailand |
Indonesia |
USA |
UK |
Italy |
Holland |
| 1995 |
67.7 |
40.79 |
5.69 |
6.7 |
8.55 |
1.54 |
2.35 |
2.77 |
| 1996 |
42.19 |
21.57 |
5.72 |
8.72 |
7.85 |
0.85 |
2.05 |
0.7 |
| 1997 |
42.18 |
16.27 |
4.46 |
6.93 |
8.4 |
0.83 |
1.77 |
2.11 |
| 1998 |
30.71 |
5.91 |
4.98 |
1.36 |
9.6 |
0.66 |
2.42 |
2.9 |
| 1999 |
26.93 |
5.09 |
5.56 |
2.3 |
12.14 |
0.87 |
4.03 |
4.19 |
| 2000 |
27.99 |
5.31 |
5.83 |
3.22 |
12.96 |
9.60 |
3.42 |
2.49 |
- The filler in paper industry is the largest consumption field of Chinese
talc. The 50-60% of the exported talc was used as paper filler. But
because of the consideration on the cost and environmental protection,
Asian paper industry have been switching to neutral or alkaline paper-making
since later 1990s, resulting in the decline of talc as filler. The talc
used as paper filler have dropped by 30% during the past ten years in
Asia, and it is expected a larger dropping will occur within the next
five to seven years.
- China has been exporting a large quantity of paper filler grade talc,
of which the principal raw materials are soapstones or chlorite. Before
1996,all such kinds of minerals were exported in the name of "Talc",
as there was no meaning to distinguish the difference between talc and
these minerals. But after 1996 when Chinese government extended charged
quota to the talc export, while soapstone, and chlorite were not included,
the exporters had to declare the formal "paper filler grade talc"
at Customs as their original names of soapstone or chlorite. Therefore
the talc export statistics after 1996 did not include the export of
soapstone and chlorite. This is an important reason for the appearent
decline of the talcum export after 1996 since about 250,000-300,000
paper filler grade talc have been exporting annually.
In contrast with the declining trend in Asian market, the talc export
to North America and West Europe have been increasing steadily after 1996(refer
to table 1). This was driven by the increasing demand for Chinese white
talc, which was used to produce talc-filler polypropylene for in automobile
industry.
2.IMPORTING COUNTRIES/REGIONS
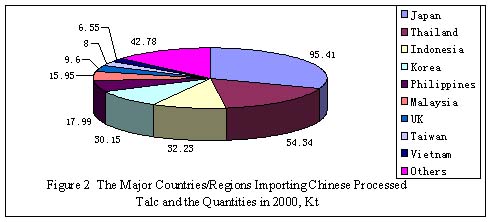
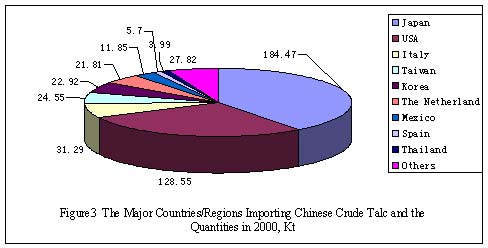
There were 74 countries/regions importing Chinese talc in 2000. Figure
2 illustrates the major countries/regions importing Chinese processed
talc, and Figure 3 the major countries/regions importing Chinese crude
talc. Japan, Thailand, Korea, Indonesia, Philippines, and Malaysia were
the leading importers of Chinese processed talc,while Japan, USA, Italy,
Taiwan, and Korea were the leading importers of Chinese crude talc.
Figure 4 illustrates the average prices of crude talc exported to some
countries. In 1994, the prices to Japan and Korea were much lower than
the prices to USA and Western European countries because Japan and Korea
imported a large quantity of low grade talc chips used as filler in paper
industry at low prices, while USA and the Western Europe imported the
upper grade lump talc at high prices. But with the declining of talc filler
in paper industry in Asia, the requirement for talc chips dropped greatly
in recent years. On the other hand, with the developing of PP plastic
in Asia, the requirement for high grade lump talc was increasing. The
price differences between Asian market and USA, Western European markets
are narrowing.
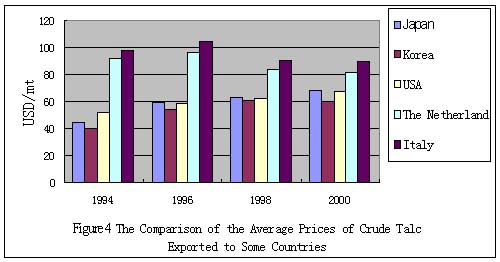
Table 2 shows the proportion of Chinese talc export to Asia, North America,
West Europe, and other regions respectively. In 1984, the 92.6% of Chinese
talc was destined to Asia. Only 6.2%, 0.7%, and 0.5% were exported to
West Europe, North America, and other regions respectively. These data
indicated the main market for Chinese talc was in Asia at that time. The
situation had changed later on. Asian market shares dropped to 85.8%,
while total shares of other market shares went up to 14.2% in 1994. Asian
market share further dropped to 65.2% in 1999, the market shares of West
Europe, North America, went up to 16%, and 17% respectively. Both the
West Europe and North America were the fastest growing markets for Chinese
Talc, while the Asian market was shrinking.
Comparing to that of 1999,the Asian market share recovered to 68% in
2000. The American market share was stable, however, the West European
market share dropped by 5.1%.
Table 2 The Proportion of Chinese Talc Export to Various Markets, %
| Year |
Asia |
West Europe |
North America |
Other Regions |
| 1984 |
8206 |
6.2 |
0.7 |
0.5 |
| 1994 |
85.8 |
2.8 |
6.1 |
5.3 |
| 1999 |
65.2 |
16.0 |
17.8 |
1.0 |
| 2000 |
68.0 |
10.9 |
17.2 |
3.9 |
3.THE PRODUCING DISTRICTS AND COMPANIES
Despite talc deposits are found in 15 Chinese provinces, most of the export
quantity come from the provinces of Liaoning, Shandong, and Guangxi where
the talc reserves are larger and the qualities are better. Figure 5 illustrates
the talc export from the above three provinces between 1996 and 2000.
Liaoning was the largest talc exporter . More than half of the export
came from Liaoning. Guangxi was the second largest exporter. Shandong
was the third one. But it is noted the export of both Liaoning and Shandong
were dropping, while the export of Guangxi was going up during the past
five years. This clearly shows the potential of Guangxi talc, and it is
expected the growing trend will continue after 2000.
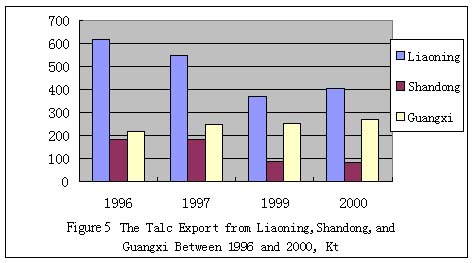
Table 3,and 4 show the export proportion of processed talc, and crude
talc from the three provinces. The 59.6-67.6% processed talc, and the
46.3-51.1% crude talc came from Liaoning. Liaoning was the largest exporter
for both processed and crude talc. But the proportion difference between
Liaoning and Guangxi is narrowing for the export of both crude and processed
talc. Table 5 lists the major Chinese talc producers.
Table 3 The Proportions of the processed Talc Exported from the Three
Provinces,%
| |
1996 |
1997 |
1999 |
2000 |
| Liaoning |
51.1 |
46.3 |
47.7 |
48.1 |
| Shandong |
15.6 |
15.7 |
9 |
8.6 |
| Guangxi |
33.3 |
38 |
43.3 |
43.3 |
Table 4 The Proportions of the Crude Talc Exported from the Three Provinces,%
| |
1996 |
1997 |
1999 |
2000 |
| Liaoning |
67.6 |
64.5 |
59.5 |
61.8 |
| Shandong |
19.7 |
21.5 |
16.6 |
13.3 |
| Guangxi |
12.7 |
14 |
23.9 |
24.9 |
Table 5 The Major Chinese Talcum Producers
Liaoning Aihai Talc Co Ltd
Haichen Beihai Minerals Co Ltd
Haichen Shuiquan Talcum Mining Co Ltd
Haichen Pailou Talc Co Ltd
Shandong Pingdu Talc Co Ltd
Shandong Laizhou Talc Co Ltd
Guilin Guiguang Talcum Development Co Ltd
Guangxi Longguang Talcum Development Co Ltd
Guangxi Longsheng Huamei Talc Development Co Ltd
--------------------------------------------------------
4.EXPORT QUOTA
Chinese talc export was subject to the quota long time ago. But the quota
was not charged until 1996.The exporters got the quota by bidding in the
"open tender", and/or by the distribution in the "agreement
tender" automatically. Figure 6 shows the quota market price since
1996.
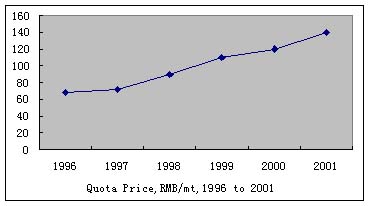
It is noted the market prices were going up continuously. The reasons
for the continuous increasing of the prices were very completed, but the
following two points are crucial:
- The quota quantity was less than the actual requirement.
- The exporters had to offer a higher price in "open tender"
to ensure to get the quota, in order to keep the continuity of exporting,
and fight for advantage positions in next year "agreement tender"
to get cheaper quotas.
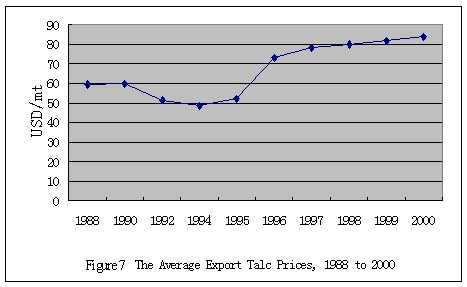
Figure 7 shows the average export talc price between 1988 and 2000. In
1990s the price went down and down until 1996 when the quota was charged,
then the price recovered continuously. Besides the quota, the increases
of mining, processing, and the domestic transportation costs were other
factors pushing the price upwards.
Table 6 shows the proportion of quota costs in the FOB Prices of some
typical Haichen Talc powder. The quota costs toke not small shares in
the export prices, especially for the low grade talc.
Table 6 The Proportion of Export Quota Cost in FOB Bayuquan Price in
2000,%
| 1250 MESH MICRONIZED POWDER |
4-8% |
HAICHEN TALC POWDER SUPER GRADE
|
10-13% |
| HAICHEN TALC POWDER NO.1 |
11-15% |
| LIAONING TALC POWDER NO.2 |
19-23% |
IMPORT
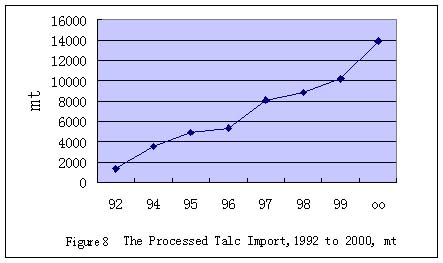
Figure 8 shows the Chinese talc import between 1992 and 2000.It is surprised
of as the largest talc producer and exporter, China's import has been
increasing rapidly since 1992 with the annual rate of 91.5%. In 1992,
the imported quantity was only 1376 mt, while in 2000 it reached 13.7
Kt, amounting to USD6.83 million. The import talc were all micronized
powder at the price more than USD400/mt, which was more than the double
price of Chinese export for the same grade. The products were mainly imported
from Taiwan, USA, Japan, Belgium, and Norway.
Before 1990s,China had few requirements for micronized talc or other
sophisticated products. The 325 mesh powder was the standard product required.
Since 1980s, China imported some industrial lines which using micronized
talc. The designed talc to be used in these lines were based on the overseas
talc products. When these lines operated in China, they continued to use
the talc recommended by the designers ,which was processed in overseas.
Besides, some of Chinese industries, such as automobiles, paint, plastic,
developed rapidly in recent years, which also require the micronized and
sophisticated talc.This is another factor stimulating the Chinese talc
import.
OUTLOOK
Despite talc is found in 15 provinces, Larger reserves were found in Liaoning,
Jiangxi, Shandong, Guangxi, and Qinghai. The total reserves of above five
provinces account for more than the 94% of Chinese talc reserve. The largest
talc reserve is found in Jiangxi, however,the talc there is in black.
The white talc mainly comes from Liaoning, Shandong, and Guangxi.
China dominates in white talc. Although talc is widely distributed in
the world, America, Europe, and Asia all having large reserves, only a
limited quantity of the reserves is white talc with whiteness more than
85%. The quantity with whiteness over the 90% is rare. The world output
of the talc with whiteness over 90%, except Chinese output, is only about
30,000mt. China has the largest white talc reserves and output in the
world. The annual output of talc with whiteness over the 88% is about
350 Kt, and that with whiteness over 85% is about 1.2 million mt. Chinese
white talc enjoys a good reputation for its high quality and competitive
price. Most of the white talc in the world originates from China although
some of them are processed in other countries. No white talc from any
other country is able to compete with Chinese product in regard to the
quantity and price. Table 7 lists the principal upper grade Chinese white
talc:
Table 7 The Principal Upper Grade Chinese Crude Talc
| Grade |
Whiteness,% |
| Haichen Lumps No.1 |
94 |
| Haichen Lumps No.2 |
92 |
Haichen Lumps No.3
|
86-88 |
| Guangxi Super Lumps |
92 |
| Guangxi Lumps No.1 |
88-90 |
| Guangxi Lumps No.2 |
85-88 |
| Pingdu Super Lumps |
90-92 |
| Pingdu Lumps No.1 |
85-90 |
| Laizhou Super Lumps |
90 |
| Laizhou Lumps No.1 |
85 |
Before 1993, Chinese talc output was between 700 to 900 Kt. In 1994 it
went up to 1.34 million tones, and in 1990 it reached the peak of 2.54
millions mt. But because of the excessive mining in the last two decades,
both the reservation and the output have been dropping during the 1990s.
The output of lump talc dropped even faster comparing to talc chips, and
the quality went down as well. The current annual talc output is less
than 2 millions mt. It is forecast the output will drop to 1.7 millions
mt within the next 3 to 5 years. Both the mining cost and the market price
will increase. This trend appeared clearly in 2001.It is expected Chinese
talc price will increase by USD5-15/mt within the next 3 to 5 years, which,however,
should be in the acceptable scope when considering its unique quality.
With more and more application of talc filler PP in automobile industry,
the world market will have larger requirement for talc with high and medium
whiteness. Within the next 3 to 5 years, the world market will require
about 800,000 Chinese talc annually(not including the paper making talc).
Although Chinese white talc will continue dominate the world market,
it is unrealistically optimistic to think that Chinese talc will enter
a bright ear, when considering the following factors:
- The Chinese talc reserves are decentralized widely. There are hundreds
of independent mines and processors. Talc producers and traders compete
with each other from the low grade to the top grade products. Although
some upper grades talc obviously falls short of the demand, the companies
still compete each other for export, as they do not dare to lose the
foreign customers and indulge in fantasy that some day more talc will
appear in their mines. The majority of producers' revenues keep in the
lowest level, which are only enough for surviving, not to mention the
development. If there is no reorganization or merging among the major
producers, the current malignant competition will not be stopped. Unfortunately,
until now no positive trend appears, although soon or later it will
do.
- Despite the export price have gone up since 1996 when the quota was
charged, Majority money resulting from the price increase was collected
by the government in the name of quota charges. Most talc producers
have no obvious profits increase ,which is urgently needed for the mines'
developments.
The 60% of Chinese talc are in chip form, which main application is
as paper filler in Asian paper industry. Within the next 3 to 7 years,
the acid paper making will be replaced by neutral or alkaline paper
making in Asia. Talc has to withdraw from the paper filler market soon
or later. If no new applications can be found, Chinese low grade talc
may face a serious decline in sales.
It is a remarkable achievement in recent years that most of the Chinese
leading talc producers mastered the processing technology of micronized
talc. The quality of the micronized product is good enough to be accepted
by most consumers, and the price is the most competitive in the world.
The standard product is 800mesh, 1250mesh, 2500mesh,or even finer. More
and more orders have been placed since 1999. In 2001 most producers are
in full operation. The output of micronized powder was 90,000 mt in 2000,
and will be about 100,000 mt in 2001.It is expected the output will be
over 120,000 mt within the next 2 years.
In summary, the supply of the upper grade lump talc will fall short of
demand ,while the low grade talc will still be a drug on the market. The
output of micronized products will continue to increase and find more
consumers. The following is the forecast of the principal markets:
- North America,and West Europe
These two markets mainly require Chinese top lump talc and top powder
products. As the output of lump talc is decreasing, it is impossible
to increase the export anymore, the supply will fall short of demand,
the price will go up. But the supply of upper grade powder will have
not much problems. Chinese producers prefer to supply high value-added
powder products rather than the lump in order to get a proper profits.
Also the upper powder product can be made partially from top grade talc
chip, which is available at a very cheap price.
- Japan and Korea
Currently Japan and Korea are the largest importers of Chinese talc.
But the import will drop quickly in the near future, because the quantity
of paper filler grade talc will go down dramatically,although it will
be partially offset by the increasing requirement of upper grade products,
especially the micronized talc.
- South East Asia
South East Asia market mainly requires low to medium grade products.
The supply of these products will be sufficient, the price will be steady.
South East Asia will not have more requirements for lump talc, however
it is the largest potential market for Chinese micronized products.
- China
The paper filler market will continue to shrink, however, the requirements
for upper grade talc products will increase greatly in the field of
plastic, paint, pharmaceutics, and cosmetics. In contrast with the past,
it is a significant the talc sale profits inside China are higher than
the export ones nowadays. What more the domestic trade is simple, which
has no need for quota, the currency control, and so on. The leading
Chinese producers are turning more attentions to the domestic market.
In the next few years, micronized and pharmaceutical grade talc will
be the two grades with fastest growing rates in sales.
|