Natural Vitamin E(tocopherol) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Natural Vitamin E (Tocopherol) is derived from soybean oil, as nature’s fat-soluble antioxidant constitutes: Alpha-tocopherol, Beta-tocopherol, Gamma-tocopherol, Delta-tocopherol. Beta-tocopherol exists in concentrations too low to have any practical significance, free of solvent residue and metal ion. Gamma and Delta-tocopherols are known primarily for their antioxidant properties. Being used as antioxidant, their physiological activities are: Delta > Beta > Gamma > Alpha. Nowadays, Natural Vitamin E is divided into Mixed Tocopherol (Low alpha-tocopherol) and Tocopherol (High alpha-tocopherol). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
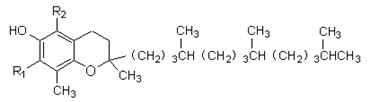
Alpha-tocopherol: R1=R2=CH3 Beta-tocopherol: R1=H, R2=CH3 Gamma-tocopherol: R1=CH3 R2=H Delta-tocopherol: R1=R2=H |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use | In food/pharmacy industry
The difference between natural and synthetic Vitamin E is mainly on Physiological activity and toxicity- C Proven by test with mice, U.S.FDA generally considers natural Vitamin E as safe and ranked into GRAS, while synthetic Vitamin E contains LD50 of 5g/kg. When used as nutrition fortifier, the physiological activity of natural alpha Vitamin E is 1.49 times of that of synthetic product. The Natural VE we extracted is in accordance with the Alpha-tocopherol concentrate Standard of U.S.A. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Food Chemical Codex (FCC IV) as follows: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Induction | Sodium Saccharin is 500 times sweet as that of sucrose; conform to the GB4578-84 standard of food additive in P.R.C., the standard of BP98, BP2001, and American Pharmacopoeia USP24, and USP25 version. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||